
 Heavy metal poisoning, or some level of metal toxicity, is surprisingly common. These toxic metals are present throughout our environment and can be very difficult to avoid. However, being properly informed about the health effects of toxic metals, the most common ones and where they typically are in the environment, and methods for detoxifying these elements from the body or preventing their absorption in the first place can go a long way towards protecting you and your family from these dangers.
Heavy metal poisoning, or some level of metal toxicity, is surprisingly common. These toxic metals are present throughout our environment and can be very difficult to avoid. However, being properly informed about the health effects of toxic metals, the most common ones and where they typically are in the environment, and methods for detoxifying these elements from the body or preventing their absorption in the first place can go a long way towards protecting you and your family from these dangers.
Toxic metals are metallic substances that are harmful to one’s health. Most people are familiar with heavy metals, such as mercury. However, while they are sometimes used interchangeably, heavy metals and toxic metals are not necessarily the same thing. Iron, for example, is a heavy metal that is necessary for healthy red blood cells, while bismuth is also a heavy metal with minimal toxic effect. Beryllium, on the other hand, is not a heavy metal, but is a metal that can cause lung and skin problems in industrial workers who may be exposed, and is thus a toxic metal. In some cases, essential trace elements can become toxic in high doses, as in the case of copper. They can also be toxic in certain forms; Chromium(III), for example, is a necessary mineral, while chromium(IV) is a known carcinogen.
The level of toxicity of any element depends directly on its solubility. Insoluble metals display only marginal, if any, toxicity to the body. Insoluble metals are generally not toxic, simply because they are so difficult for the body to absorb. Some toxic metals can be even more toxic when they occur in particularly soluble forms, such as methylmercury, or tetraethyl lead. Toxic metals cannot be easily excreted and tend to bioaccumulate, that is, to build up in the tissue. This is why even miniscule amounts are of concern. Repeated exposure to tiny amounts adds up to a lot of toxicity.
Neuroendocrinology examines the interaction of the nervous and endocrine systems and how they work together to regulate various physiological functions. Neuroendocrinology was developed after the discovery that the brain, and in particular the hypothalamus, directly controls the release of hormones from the pituitary gland.
The NeuroEndoMetabolic (NEM) perspective takes this idea of various systems in the body working together to the next level. The NEM system describes how the nervous, endocrine, and metabolic systems work together in conjunction with various other systems and organs to regulate the body’s reaction to stress. It is through this perspective that we are able to describe the mechanisms behind all stages of adrenal fatigue, from mild fatigue to full burnout.
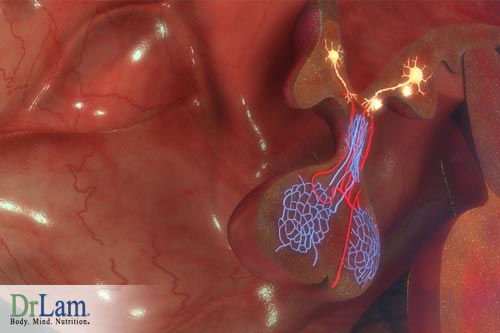 Conventional ideas of how the body responds to stress focused on the HPA-axis, which refers to the interactions of the hypothalamus, the pituitary gland, and the adrenal glands. These organs are at the core of the stress response, and dysfunction in one or more of these explains many, but not all, of the symptoms of adrenal fatigue. It is the symptoms that cannot be explained this way that have prompted some scientists and doctors to look more closely at how stress affects the body as a whole. They discovered a strong connection between the metabolic system and the HPA-axis. Dysfunction in the metabolism can impair the effectiveness of the stress response, while prolonged stress can lead to metabolic disturbances. Thus a healthy stress response depends not only on a healthy neuroendocrine system, but also on a healthy metabolism.
Conventional ideas of how the body responds to stress focused on the HPA-axis, which refers to the interactions of the hypothalamus, the pituitary gland, and the adrenal glands. These organs are at the core of the stress response, and dysfunction in one or more of these explains many, but not all, of the symptoms of adrenal fatigue. It is the symptoms that cannot be explained this way that have prompted some scientists and doctors to look more closely at how stress affects the body as a whole. They discovered a strong connection between the metabolic system and the HPA-axis. Dysfunction in the metabolism can impair the effectiveness of the stress response, while prolonged stress can lead to metabolic disturbances. Thus a healthy stress response depends not only on a healthy neuroendocrine system, but also on a healthy metabolism.
In the early stages of adrenal fatigue, many people respond to fatigue by pushing through, perhaps with the assistance of caffeine or other substances. As adrenal fatigue advances, sufferers may seek the assistance of a healthcare professional, who may recommend medications to manage symptoms. However, correcting the problem behind adrenal fatigue requires supporting the NEM system through rest, good nutrition, and removal of toxins.
Your body has a built in detoxification system that continuously removes most toxins and heavy metal poisoning. However, not only are we exposed to far more toxins than in ages past, but toxic metals are very difficult to remove, especially without proper nutrition through fresh, whole, minimally processed, and organically grown foods. Primary routes of detoxification are through the liver, intestines, skin, lungs, kidneys, and lymph nodes.
The liver removes toxins from the body in several ways, including:
Toxins removed by the liver are released through the bile ducts into the small intestine. Supporting the liver is crucial to the detoxification process.
Your digestive tract does more than simply extract nutrients from the food you eat and excrete what is left over. When the digestive tract is healthy, it allows nutrients to pass through to the bloodstream, and absorbs toxins from the bloodstream to be eliminated. When the digestive tract is not working optimally, it cannot effectively remove toxins and may allow partially undigested food particles to enter the bloodstream. In addition, food and toxins that cannot be eliminated begin to ferment and putrefy, releasing additional toxins.
While most people don’t think of the skin as an organ, it’s actually the largest organ in the body. The skin is able to remove water soluble toxins such as protein residue and uric acid through the sweat glands.
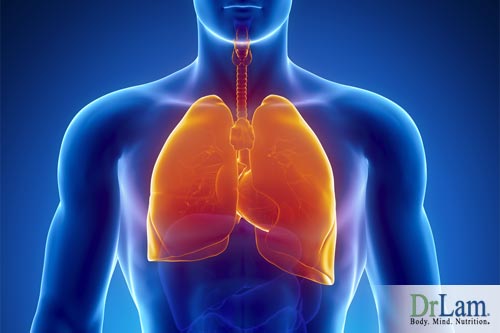 The lungs are primarily responsible for removing carbon dioxide and other gaseous toxins through exhalation. When the membranes are healthy, these are the only toxins removed by the lungs. However, when the membranes are irritated, toxins from the blood stream may squeeze through the membrane and be coughed up as phlegm.
The lungs are primarily responsible for removing carbon dioxide and other gaseous toxins through exhalation. When the membranes are healthy, these are the only toxins removed by the lungs. However, when the membranes are irritated, toxins from the blood stream may squeeze through the membrane and be coughed up as phlegm.
Like the liver, the kidneys filter harmful substances from the blood. Toxins removed by the kidneys are excreted in the urine. In order for the kidneys to function efficiently, blood pressure should be within a healthy range, neither too high nor too low, and the body should be well hydrated.
Lymph is created when the fluid surrounding the cells is taken up by the capillaries, similar to the capillaries that carry blood. Lymph flows through these capillaries to larger vessels to the lymph nodes, and ultimately to the subclavian vein, where it mixes with the blood. Lymph transports excess protein from the cells to the bloodstream, and can pick up bacteria and metastatic cancer cells for destruction in the lymph nodes.
Many minerals are toxic, but most of them are relatively rare and your risk of exposure is very slim unless you work in an industry that involves their use. There are five, however, that people in the modern world are frequently exposed to. These represent some of the biggest risks for heavy metal poisoning in the modern world.
Mercury exposure is one of the worst heavy metal poisoning simply because, despite it being a known neurotoxin, it is still a pervasive part of our lives. Dental fillings, fish, and even some vaccines still contain traces of thimerosal, a preservative containing 50 percent mercury by weight. You can minimize your exposure to mercury by asking for alternative filling materials when you have dental work done, by asking for thimerosal-free vaccines, and by avoiding the varieties of fish that are known to have the highest mercury concentrations, such as shark, swordfish, mackerel, and some varieties of tuna.
If you have any ‘silver’ fillings in your teeth, those fillings are as much as 50 percent mercury by weight. Mercury in these fillings has been ruled safe by the American Dental Association. However, while just over 75 percent of the American population has at least one mercury amalgam filling, 95 percent of people with disorders of the central nervous system have them.
Many people who have had their mercury fillings removed have reported significant improvements in these and other health conditions within weeks of the procedure.
However, if you are considering having mercury fillings removed, talk with your dentist to find out what safety precautions are used to contain and minimize your exposure to mercury that may be released in the process. It is very important for both the dentist and the client to have the bio-fumes vacuumed up before they are exposed to the mercury vapor. If you have AFS, removal must be timed properly to avoid trigger adrenal crashes.
You can stop accumulating mercury by avoiding most fish and shellfish, especially those along coastal waters, as they are universally contaminated unless you are in pristine waters like Alaska. Pregnant and lactating women should avoid tuna, shark, king mackerel, ahi, mahi-mahi, halibut, and other large fish.
 Lead is a heavy metal that naturally occurs in the earth’s crust. As long as it remains there, it’s perfectly safe. However, through mining and industry, lead heavy metal poisoning has become a significant concern, especially in children. As a result, lead was removed from household paint and gasoline in the mid-1970s, though an estimated 64 million homes built before 1978 may still have lead-based paint. Lead is also used in the manufacture of products including batteries, rubber products, and glass. In some areas, drinking water may be contaminated with lead. Lead can also enter the water supply through lead pipes or be released into the atmosphere during the demolition of industrial buildings.
Lead is a heavy metal that naturally occurs in the earth’s crust. As long as it remains there, it’s perfectly safe. However, through mining and industry, lead heavy metal poisoning has become a significant concern, especially in children. As a result, lead was removed from household paint and gasoline in the mid-1970s, though an estimated 64 million homes built before 1978 may still have lead-based paint. Lead is also used in the manufacture of products including batteries, rubber products, and glass. In some areas, drinking water may be contaminated with lead. Lead can also enter the water supply through lead pipes or be released into the atmosphere during the demolition of industrial buildings.
Low levels of lead in children can cause learning disabilities, developmental delays, behavioral issues, loss of appetite, nausea, abdominal pain, and other issues. Lead exposure in all ages can damage the kidneys and the nervous system, reproductive system, and cardiovascular system. It can also cause cognitive impairment, irritability, and even hearing loss and tooth decay.
Avoiding lead heavy metal poisoning isn’t easy, especially if you have small children and live in a house built before 1978. You can minimize your exposure by leaving your shoes outside when you enter the house, wet-mopping and wiping down surfaces frequently, and using a water filter. If you have children, you can minimize their exposure by washing their hands and toys frequently and by keeping them away from lead-based paint as much as possible. Glazes used on cookware in some countries still contain lead that can come off onto the food.
Aluminum is another toxic metal that is found in many everyday items, including: antiperspirant, antacids, medications, some baking powders and other processed foods, and some feminine products. It can also be released into food through the use of aluminum cookware, aluminum cans, and foil. Aluminum heavy metal poisoning has been linked to a variety of serious health conditions, including: osteoporosis, Alzheimer’s disease, anemia, cognitive difficulties, impaired liver, and impaired kidney function. Avoid sea salt which often has aluminum added as an anti-caking agent. Use sea salt instead. Some cities add aluminum to their tap water to remove dirt particles. Check with your city to ensure this does not happen to your water source.
Arsenic can be found in organic and inorganic compounds and functions as a pesticide, bactericide, and fungicide. Organic arsenic is often used as a pesticide in agricultural applications, and inorganic arsenic is commonly used to preserve wood. Arsenic is naturally occurring in apples and some other fruits and has been found in some brands of rice. Many arsenic compounds are water-soluble and can be found next to occupational hazards, and contaminated water, especially well water. Other potential sources of exposure include sawdust or smoke from wood treated with arsenic. In some countries, it can be legally added to chicken feed, resulting in arsenic in eggs.
 Arsenic can also be leached into the soil from livestock operations, affecting the food chain downstream. Use organically grown produce to avoid arsenic that may be used in pesticides.
Arsenic can also be leached into the soil from livestock operations, affecting the food chain downstream. Use organically grown produce to avoid arsenic that may be used in pesticides.
Low levels of arsenic heavy metal poisoning exposure can cause nausea, vomiting, decreased blood cell production, cardiovascular damage, nerve damage, and has been linked to certain cancers, including bladder, lung, skin, kidney, liver, and prostate cancers.
Cadmium is a naturally occurring metal that has been shown to both damage the DNA and inhibit the body’s ability to repair damaged DNA, making it a known carcinogen. It toughens the vascular structure. Some studies suggest it can also cause hypertension and may damage the liver, kidneys, and central nervous system.
Cadmium is released as a result of mining, burning coal, and manufacturing certain goods. Cadmium is water-soluble and binds with soil particles. As a result, it can contaminate water sources and food grown in contaminated soil. In industrial areas and areas where waste is frequently burned, it can also be found in the air.
Cigarette smoke contains high amounts of cadmium heavy metal poisoning, and smokers are exposed to approximately twice as much cadmium as nonsmokers. It is known as the “macho” mineral as it is one often found in higher levels in people that have exposure to violent jobs, such as law enforcement.
Cadmium replaces zinc in male testicles and tends to accumulate in people who have frequent orgasms. Male and female sexual fluids are rich in zinc and a lesser degree, cadmium.
Not to be forgotten is cadmium in the air, which comes from brake linings of cars. Those who live near heavy traffic areas should be concerned. It is also present in small amount in cigarettes, marijuana, and cannabis oil. Cadmium can also boost sodium level.
Antimony is a metal found in the earth’s crust. It is mainly used in industrial production, especially in making materials fire-retardant, but it also has therapeutic uses. The effects of antimony toxicity depend on the way antimony enters the system. If it is inhaled, it can cause irritation, bronchitis, emphysema, pneumoconiosis, adhesions, and inactive tuberculosis. It has been linked with lung tumors in rats and is thought to also be carcinogenic to humans. Skin exposure can cause a type of dermatitis that is aggravated by warm weather and relieved by cooler weather. It has also been linked to genotoxicity (damage to your genes) as well as issues with reproductive cycles and fertility in women. If ingested orally, it can cause nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and diarrhea.
Most antimony heavy metal poisoning happens to people working in antimony production, though this is currently less prevalent due to stricter occupational health regulations.  There have also been cases of exposure through certain types of products fire-proofed with antimony, such as baby cots and firefighting uniforms.
There have also been cases of exposure through certain types of products fire-proofed with antimony, such as baby cots and firefighting uniforms.
Therapeutically, antimony compounds are used in the treatment of two parasitic diseases: leishmaniasis and schistosomiasis. The side effects of these treatments are pancreatitis and cardiotoxicity. Toxicity from therapeutic antimony can be prevented through strict quality control of each batch of the drug.
Barium is a silvery-white metal found in the earth. It combines with other elements to form certain kinds of compounds that are used for things like rat poison, in x-ray imaging and radiology, in enemas, and for industrial production. It can also be found in cigarette smoke. Barium toxicity can cause arrhythmias, muscle twitching, high blood pressure, low blood potassium, gastrointestinal issues, respiratory problems, and even paralysis. If the toxicity is severe or chronic it could lead to kidney failure, respiratory failure, multiple sclerosis, and death.
Heavy metal poisoning exposure to barium can occur through environmental contamination and the contamination of groundwater, both of which are most likely to be caused by industrial production. Also, if you’re a smoker, you are at higher risk for barium toxicity. There have also been cases of barium toxicity experienced after certain medical procedures, such as with barium enemas. There are lab tests that can tell you the barium levels in your system. The usual procedure to neutralize barium is through potassium supplements. To prevent barium toxicity, you can consider eating organic foods, using water filters, and quitting smoking. You can also check if you live in an area with a higher risk of industrial barium contamination.
Bismuth compounds are found in many pharmaceuticals, including over-the-counter drugs, especially those that treat an upset stomach. Bismuth is also used in making shotgun pellets and fishing anchors, and in some cosmetics. Though it is always preferable to avoid products with toxic metals as much as possible, very mild bismuth exposure is considered harmless.
Most bismuth toxicity happens to people working with the metal regularly, such as workers who use bismuth-containing products like solder – a metal alloy that is used to bond two pieces of metal, as with plumbing for example. Overdoing it with medications and cosmetics containing the element can also lead to toxicity in the body, and so it goes without saying that you should try your best to lessen your use of these products. The greater concern is actually not in the bismuth toxicity itself, but in the fact that to have bismuth heavy metal poisoning you have probably also been exposed to other, more dangerous, toxic metals.
Symptoms of bismuth toxicity include headaches and nausea. In some studies, it has been shown to contribute to male infertility. Children recovering from chickenpox may develop Reye’s syndrome – a dangerous swelling of the brain and liver – if they are exposed to bismuth in the process.
 Cesium is a silvery-white metal found in the environment in naturally occurring compounds, mostly in soil and rocks. It is released into the environment through the natural erosion of minerals and also through the mining of certain ores. Cesium compounds are not widely used for commercial purposes - their main use being in the making of atomic clocks, scintillation counters, and in the coating of tungsten filaments.
Cesium is a silvery-white metal found in the environment in naturally occurring compounds, mostly in soil and rocks. It is released into the environment through the natural erosion of minerals and also through the mining of certain ores. Cesium compounds are not widely used for commercial purposes - their main use being in the making of atomic clocks, scintillation counters, and in the coating of tungsten filaments.
Heavy metal poisoning exposure to stable cesium can happen by eating food or drinking water containing it, but there’s not much to worry about with this, as its concentration is usually very low. The higher risk belongs to workers who produce or use cesium industrially.
Radioactive cesium is produced when nuclear weapons are exploded or in the regular operations of nuclear power plants. It is released into the environment through these mechanisms, as well as through nuclear power plant accidents. Exposure to radioactive cesium can cause cell damage. Those who work in nuclear power plants and those who have been exposed to the radioactivity of nuclear power reactor accidents – such as Chernobyl and Windscale – are more at risk. Even then, cesium was only a small part of the overall reactivity released from these accidents.
Gadolinium is a rare earth metal that is only found naturally in an oxidized form. It is used to make other metals more workable. It is also used in x-rays and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). In MRIs, gadolinium chelates are used as contrast agents, taken orally or intravenously, to help sharpen the visibility of the internal parts of the body being scanned.
Up until recently, they were thought to be very safe if taken below a certain dose except in the case of patients with renal insufficiency. With these specific patients, a link has been observed between these contrast agents and nephrogenic systemic fibrosis – a type of fibrosis that affects the internal organs and skin.
Lately, gadolinium has been found in the organs and tissues of those that don’t have renal insufficiency. The implications of these observations are not known. The possibility and effects of gadolinium toxicity have not yet been tested or recorded enough to create a full picture. Yet, due to these new findings, the FDA announced in 2015 that it will be investigating the possibility of gadolinium deposits in the brain from repeated exposure to MRIs. So far, in vivo studies have shown that gadolinium heavy metal poisoning causes damage not only to kidney cells but also damage and death to liver and lung cells as well.
Gallium is a silvery metal that is liquid at room temperature. It is one of four such types of liquid metals, with the others being mercury, cesium, and rubidium. Out of the four, it is the least reactive and least toxic. It is mainly used in the production of electronics. Gallium alloys are also sometimes used by dentists as replacements for amalgam fillings that contain mercury.
 Not much is known about gallium toxicity, as there have been very few cases of it. On a day-to-day basis, the use of gallium-containing electronics does not lead to gallium heavy metal poisoning. The risk is higher for producers of semiconductors – as there could be accidental exposure during that process.
Not much is known about gallium toxicity, as there have been very few cases of it. On a day-to-day basis, the use of gallium-containing electronics does not lead to gallium heavy metal poisoning. The risk is higher for producers of semiconductors – as there could be accidental exposure during that process.
In one case of acute gallium poisoning, the patient first presented symptoms of dermatitis, but then quickly worsened to tremors, vertigo, tachycardia, blackouts, and dyspnea. Eventually, the poisoning leads to the patient’s death. Although in this particular case the patient’s death may have been prevented with more effective medical care, what was striking was the speed at which morbidity was reached.
At the moment, there is no clear exposure limit set, and there are no defined medical protocols for treating gallium toxicity. To be safe, you can consider asking your dentist about the different options available if you intend on replacing your amalgam fillings.
This is one of the more common toxic risks, as iron tablets are readily available without a prescription. The risk of iron toxicity is higher for children as they sometimes confuse iron pills for candies and can ingest a few of them in one sitting. This is why it is very important to keep all kinds of medications and supplements out of reach of children at all times.
Iron is an irritant to the stomach and can corrode the intestinal lining. Symptoms of iron heavy metal poisoning include vomiting, diarrhea, bloody stool, bloody vomit, abdominal pain, and dehydration. It usually takes six hours for the symptoms to begin to appear after ingestion. Although it is easily treatable, if it is left untreated it can eventually lead to death. Toxicity begins at around 10 mg/kg, and anything over 50 mg/kg is considered severe.
Thallium is a very toxic heavy metal that is used in manufacturing certain types of technologies, in medicine, and as rat poison. It is also a waste product in the production of cement and in coal combustion. Thallium is very easily absorbed by the body as its similarity to potassium in charge and ionic radius allows it to enter the cells the same way potassium does.
Once in the system, it inhibits cellular respiration and disrupts calcium homeostasis. It interferes with glycolysis energy production and oxidative phosphorylation. It also binds with protein sulfhydryl groups and interacts with riboflavin. Thallium heavy metal poisoning can cause gastroenteritis as well as a very rapid and painful peripheral neuropathy and, its most observable feature, alopecia. Other signs include motor weakness and changes in mental states. It also has adverse effects on the kidneys, liver, and heart.
Traditionally, activated charcoal has been the safest method of treating thallium poisoning. From an enterohepatic perspective, it stops the cycling of thallium and causes it to be excreted in the stool. Other methods that are frequently used to chelate metals from the body, such as penicillamine, are not effective for thallium poisoning, and may even cause further damage by redistributing it through the system. In some cases, diuresis with potassium loading may help with clearing thallium through the kidneys, but this method carries the risk of aggravating cardiovascular and neurological symptoms.
If you suspect you have thallium toxicity, you must seek medical care immediately. Thankfully, with the right treatment, you can have a full recovery.
Thorium is an odorless, tasteless radioactive metal that is found in small amounts in soil, rocks, water, plants, and animals. Its main use is in the making of metals, lantern mantles, and ceramics for the aerospace industry. It is also used in nuclear reactions and as fuel in generating nuclear energy.
Although you are probably exposed to thorium in your environment through the air and in food and water, very little of it actually enters your bloodstream. Of the amount that does, much of it is expelled or excreted from your system within days. The tiny amount that remains in your system will most likely be found in your bones.
 Those at highest risk are thorium industry workers, who can end up developing pancreatic cancer, lung disease, and lung cancer. In rare cases, people who have had thorium injections for special x-ray imaging have been found to suffer from blood and liver issues, and sometimes bone cancer.
Those at highest risk are thorium industry workers, who can end up developing pancreatic cancer, lung disease, and lung cancer. In rare cases, people who have had thorium injections for special x-ray imaging have been found to suffer from blood and liver issues, and sometimes bone cancer.
If you live near a plant that uses thorium, you may be exposed to its radioactive decay products such as radium and thoron. In this case, you might have to undergo special tests to check for them in your system. Otherwise, you don’t have much to worry about regarding thorium heavy metal poisoning, as it is quite rare.
Tin is a naturally occurring metal that is used to make cans and containers, mainly for food storage. It’s also used in solder to connect pipes in plumbing and electrical circuiting. Tin compounds are even found in soap and toothpaste. This makes it one of the metals that you are most likely to be exposed to on a daily basis, so it’s important to understand when and how you might accumulate tin toxicity.
Although tin food cans are coated with enamel to keep the tin from seeping into the food, acidic foods can erode this lining and let the tin through. Also, tin has been found in seafood from certain areas. The biggest risk, however, comes from industrial plants that produce toxic waste, which can release tin into the surrounding environment. For workers in this industry, there is an increased risk of lung disease from tin exposure. Studies have shown lung tumors developing in rats that were exposed to tin inhalation, though tin has not yet been designated as carcinogenic to humans.
If you’re concerned about tin heavy metal poisoning, then you can cut down on canned foods and check if the seafood you’re consuming comes from areas with tin contamination.
Titanium is one of the most abundant metals in the earth’s crust. It is used to make jewelry, in heat exchange systems, for hip replacements, in cosmetics, and to make plane motors. It is even used as an additive in food, especially as a food coloring in sweets. Another common use for titanium is in sunscreen, and some studies assert its effectiveness in protecting the skin from UV-ray damage.
However, there are growing concerns about its usage, especially in food and cosmetics. Some studies are starting to show that titanium can indeed have negative effects on health. Lab rats exposed to titanium nanoparticle inhalation developed injuries in their lungs, including redness and emphysema. Other studies have observed titanium dioxide creating toxicity in brain cells. Titanium has also been observed to cause oxidative stress and has been designated as a possible carcinogen by the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health as well as the International Agency for Research on Cancer.
You can get tested for titanium heavy metal poisoning in your body. If you have children, it is recommended that you avoid giving them sweets with titanium additives. You can also opt for natural cosmetics.
 Tungsten is a metal found in rocks and soil as part of mineral compounds. Tungsten and tungsten alloys are used in x-ray tubes, phonographic needles, high-speed tools, turbine blades, darts, fishing weights, golf clubs, and light bulbs. They’re also used as catalysts in chemical reactions. Some tungsten compounds are used in fabric dyes and fire retardants.
Tungsten is a metal found in rocks and soil as part of mineral compounds. Tungsten and tungsten alloys are used in x-ray tubes, phonographic needles, high-speed tools, turbine blades, darts, fishing weights, golf clubs, and light bulbs. They’re also used as catalysts in chemical reactions. Some tungsten compounds are used in fabric dyes and fire retardants.
Tungsten heavy metal poisoning exposure can happen through air, water or food. People living near industrial plants that work with tungsten are exposed to more of it in their environment and, of course, the most at risk are those who work with it directly. Even though there isn’t enough data at this point, tungsten exposure is not thought of as a significant health hazard.
Most tungsten ingested or inhaled is expelled quickly from the body, and the small amount that remains a little longer is eventually excreted through urine and stool.
Tungsten toxicity has been linked to cancer, brain fog, and pulmonary fibrosis. If you believe you have been exposed to high amounts, you may want to ask your doctor for advice. For cautionary reasons, if you work with tungsten, you may want to keep your work tools away from your children. If you live near a plant that uses tungsten, check with your local health department if there is cause for concern.
Uranium is a naturally occurring metal, but it has also been produced through nuclear reactions and physics experiments. All of its isotopic forms are radioactive and exposure to uranium can have both radiological and chemical effects on health.
Uranium heavy metal poisoning can happen to you if you breathe air or eat food that contains it. The inhaled and ingested uranium enters the bloodstream and then goes through kidney filtration, which is where it can cause the most damage. If the uranium poisoning is acute, kidney failure and even death may occur. At lower levels, however, there can be some damage to kidney cells, and this can be determined through testing for dead cells and protein in the urine. Your kidneys have the ability to repair themselves if the damage is minor and you are no longer exposed to uranium.
Acute toxicity usually occurs when there is 50-100 mg of uranium in the system, and lower toxicity can be anywhere from 25-40 mg. The level of toxicity that uranium exposure can create depends on how soluble the uranium compound in question is and the route of exposure (through ingestion, inhalation, or dermal contact). Dermal contact has the least effect on health. Also, the less soluble the compound is (thus the least absorbable by the system), the less toxic it will be.
Uranium’s radiological damage is a much lower risk than its chemical damage and is usually more of a factor for workers who are exposed to uranium decay products. The main health effect of radiological exposure is an increased risk for the development of cancer later in life.
 Nickel is used in jewelry, electronics, coins, industrial machines, and magnets. Even though it is actually a known health hazard it is still used widely in industrial work such as welding, refining, and plating. Consistent exposure to nickel comes with an increased risk of neurological problems, heart disease, liver and kidney dysfunction, fertility and reproductive problems, and different kinds of cancer. It is also associated with developmental problems in children.
Nickel is used in jewelry, electronics, coins, industrial machines, and magnets. Even though it is actually a known health hazard it is still used widely in industrial work such as welding, refining, and plating. Consistent exposure to nickel comes with an increased risk of neurological problems, heart disease, liver and kidney dysfunction, fertility and reproductive problems, and different kinds of cancer. It is also associated with developmental problems in children.
Nickel toxicity has been shown to cause imbalances in the body’s metals and has adverse effects on the action and regulation of enzymes. Nickel toxicity is also a source of oxidative stress.
Although the risk of exposure is higher for those who work with nickel, people who do not work with nickel can be exposed to it by wearing nickel-containing jewelry and even through the use of certain types of dental braces. Acupuncture needles may contain nickel as well. Orthodontics containing nickel can become a risk for ingestion because of their constant contact with saliva and the occasional contact with the acidity in certain types of drinks – such as sodas, alcoholic beverages, and fruit juices.
You can minimize heavy metal poisoning exposure to nickel by making sure your jewelry is nickel-free and asking your orthodontist for options regarding your braces.
 Heavy Metal Poisoning can be either acute or chronic. Acute toxicity occurs when one is exposed to a toxic metal at a high level, such as drinking contaminated water or through occupational exposure. Acute exposures are easier to identify than chronic exposures. Symptoms of acute metal toxicity include:
Heavy Metal Poisoning can be either acute or chronic. Acute toxicity occurs when one is exposed to a toxic metal at a high level, such as drinking contaminated water or through occupational exposure. Acute exposures are easier to identify than chronic exposures. Symptoms of acute metal toxicity include:
Symptoms of chronic, low level heavy metal poisoning are more common and often quite subtle and easy to dismiss. Symptoms of chronic heavy metal poisoning include:
As toxic metal levels continue to build, problems can become more serious, and cause damage to the central nervous system, cardiovascular system, gastrointestinal system, and endocrine system as well as to the lungs, kidneys, liver, and bones.
Minimizing your exposure to toxic metals starts with understanding your potential sources of exposure. Some of the most common sources of toxic metal exposure include items you come into contact with every single day without a second thought.
Water may be contaminated with many toxic metals. This may be the result of pollution or leaching from lead pipes or other plumbing components. If you think your water may be contaminated, you have two main options. You might opt for bottled water, but bottled water is not regulated as strictly as tap water and may contain just as many plastic toxins. Bottled water can also be quite expensive and may present other health hazards. A better (and potentially more budget-friendly) option is to invest in a good water filter that can filter out not only bacteria and viruses, but also chemicals and metal toxins. Reducing the risk of heavy metal poisoning.
 Aluminum, stainless steel, and nonstick cookware like teflon can all leach toxic metals into your food during cooking. Opt for glass, cast iron, titanium, or enamel cookware. Cast iron is an especially good option for those that tend to be a bit anemic, as food cooked in cast iron absorbs the iron. This is especially true for acidic foods, such as tomato-based sauces. Be aware that restaurants are required to use stainless steel cookware, so limit restaurant meals. On a related note, stainless steel water bottles and orthodontic devices can also contain toxic metals.
Aluminum, stainless steel, and nonstick cookware like teflon can all leach toxic metals into your food during cooking. Opt for glass, cast iron, titanium, or enamel cookware. Cast iron is an especially good option for those that tend to be a bit anemic, as food cooked in cast iron absorbs the iron. This is especially true for acidic foods, such as tomato-based sauces. Be aware that restaurants are required to use stainless steel cookware, so limit restaurant meals. On a related note, stainless steel water bottles and orthodontic devices can also contain toxic metals.
Many cosmetic products, especially antiperspirants, contain aluminum and other toxic metals. Women are exposed to approximately 700 chemicals daily and have no idea about it because the cosmetic industry is not regulated well. Many companies dump toxins into their products to make them more functional. However, the skin absorbs much of these toxins and has a hard time expelling them out of the body. While mercury is notorious for being absorbed by the skin, it’s not the only toxin absorbed in this way. Toxic metals in your beauty routine aren’t just sitting on top of your skin, they’re making their way in. Check labels closely and look for products that do not contain aluminum or other toxic metals. Even costume jewelry can pose a problem in those with sensitive skin.
Most toxic metals are naturally occurring, and may be found in the soil. Removing your shoes before entering your home can help to keep toxic metals out. Also, be sure to wash your hands after working in the yard or playing outdoors with children.
As discussed, seafood can be contaminated with mercury, and food cooked in certain types of cookware absorb toxic metals. However, these are only two of the ways in which the food you eat could be a source of heavy metal poisoning. Food grown in soil containing high levels of toxic metals will contain at least trace amounts of those toxic metals. Seafood may also contain cadmium, as can grains, legumes, and leafy greens. This may be one of the most difficult sources of toxic metals to avoid, as it can be difficult to know what kind of soil your food has been grown in, even when you have your own garden. If you do choose to grow some of your own food, avoid commercial pesticides and other garden chemicals and consider having your soil tested.
Cigarette smoke contains thousands of known toxic substances, including cadmium and other toxic metals. If you smoke, quit. If someone in your home smokes, encourage them to quit or insist that they smoke outside.
Some products may be contaminated with toxic metals, either because they are believed to have medicinal properties or through accidental contamination. Make sure to look for a reputable vendors for these types of products with strict quality testing.
If you work in an industry where you may be exposed to toxic metals, be sure you review the MSDS (Material Safety Data Sheet) information on the materials to which you may be exposed, and be sure to observe all safety precautions.
 Lead toxicity is of particular concern, simply because lead is nearly impossible to avoid. Lead has been banned from many applications in numerous countries, but not everywhere. Children’s toys imported from countries where lead has not been banned may contain lead, especially in the paint. Even in the United States, lead has not been banned from use in plastics, and it is frequently used to make plastic more flexible and durable.
Lead toxicity is of particular concern, simply because lead is nearly impossible to avoid. Lead has been banned from many applications in numerous countries, but not everywhere. Children’s toys imported from countries where lead has not been banned may contain lead, especially in the paint. Even in the United States, lead has not been banned from use in plastics, and it is frequently used to make plastic more flexible and durable.
Many of the symptoms of lead poisoning, such as fatigue, hyperactivity, irritability, lack of appetite, digestive distress, weight loss, and impaired cognition, can be caused by many other conditions and are easily disguised. If you live in a home painted prior to 1978 and have these symptoms, consider getting a lead blood level test and moving out of the home if your levels are elevated.
Fluoride is the subject of significant controversy in the field of dentistry. There are studies that show fluoride can strengthen teeth, while other studies cast doubt on these claims. High doses of fluoride can cause fluorosis, which can weaken the bones and discolor the teeth. Fluoride has also been shown to increase absorption of lead, aluminum and other toxic metals that can lead to heavy metal poisoning. Fluoride is added to the water supply in many municipalities, so it can be difficult to avoid completely. If you use toothpaste or other dental hygiene products containing fluoride, be very careful not to swallow it.
When people with healthy lifestyles find they experience serious health issues, get sick more often than their peers, or experience poor digestion and gastric distress, it’s possible that toxic metal overload is the cause. High levels of these metals are considered to be a medical emergency, but even low levels of toxic metal exposure can cause a host of illness symptoms, especially when exposure is frequent. Some of these metals, mercury in particular, are toxic at concentrations as low as one part per billion.
Even if you try to follow a generally healthy lifestyle, you’re being exposed to toxic metals from many different sources every single day. In fact, we’re exposed to so many toxins that babies are born with these toxic metals in their bloodstream. In 2004, the Environmental Working Group discovered that babies were born with an average of 287 toxins, including mercury, at detectable levels in their bloodstreams. These toxic metals are difficult for even a healthy body to process and remove, so they simply build up in the tissues and cells until they begin to cause or exacerbate any number of health conditions.
Removing toxic metals occurs through a process known as chelation. In cases of acute heavy metal poisoning, chelation may be done in a medical setting. Lower levels of metal toxicity may not be addressed medically, but there are some foods, supplements, and nutrients that have been shown to effectively bind with toxic metals in the body so they can be more easily removed.
 Proper nutrition is a vital component in removing toxic metals from the body. Part of the importance of proper nutrition lies in supporting those organs and systems responsible for removing toxins. Just as importantly, however, is that the body is an expert at making do with what’s available. When the body does not get enough of the essential minerals it needs to function well, it will find a way to fill the gap. This may mean using toxic metals to stand in for what is lacking. For example:
Proper nutrition is a vital component in removing toxic metals from the body. Part of the importance of proper nutrition lies in supporting those organs and systems responsible for removing toxins. Just as importantly, however, is that the body is an expert at making do with what’s available. When the body does not get enough of the essential minerals it needs to function well, it will find a way to fill the gap. This may mean using toxic metals to stand in for what is lacking. For example:
Substitutions are not a good thing when it comes to substituting lead for calcium. However, substitution is the body’s way of surviving in situations of deficiency. When the body begins substituting toxic metals for needed minerals, they cannot be removed through chelation. The only way to remove them is to replace them with the needed nutrients. This is one of many reasons why proper nutrition is so critical to the chelation process.
 Healthy adrenal function is critical to supporting a strong detoxification system and removing toxins from the body. When the adrenals are not functioning well, toxic metals can build up in the tissue. As toxic metals build up, they become an additional stressor on the adrenals, impairing their function further.
Healthy adrenal function is critical to supporting a strong detoxification system and removing toxins from the body. When the adrenals are not functioning well, toxic metals can build up in the tissue. As toxic metals build up, they become an additional stressor on the adrenals, impairing their function further.
For those with adrenal fatigue, detoxification, especially removing toxic metals, should be done very carefully to avoid reactive metabolite overload, retoxification reaction, liver congestion, and extracellular matrix pollution.
Chelation is a two stage process. First, the toxic metals must be released from the organs and tissue. Once the toxic metals have been released from the tissue, they must then be eliminated. People who suffer from adrenal fatigue have a greater load of toxins to eliminate, and less ability to effectively do so. Releasing this concentrated load of toxins, when they cannot be effectively eliminated, simply mobilizes the toxins to circulate through the body. This can lead to a sort of healing crisis in which symptoms of adrenal fatigue may become significantly worse, potentially leading to full adrenal crash.
By supporting the adrenal glands and other organs of detoxification with the right elimination pathways and correcting the nutrient balance gradually and carefully, these side effects of the chelation process can be minimized and managed.
The easiest way to support your body during detox is by getting plenty of rest, drinking plenty of clean water, and eating high quality, nutritious food. Your diet should consist primarily of foods that are natural, unprocessed or minimally processed, locally grown, seasonal, organic, and unpasteurized. Work toward eliminating sugar and sweeten with honey or maple syrup when needed. Be sure to get plenty of healthy omega-3 fatty acids, but be careful of seafood that may contain mercury.
Cilantro and chlorella have both been shown to be especially effective in binding with toxic metals and mobilizing them so they can be removed from the body. Milk thistle and dandelion root are also great herbs to help strengthen the liver and detoxify.
 While the body has several routes of detoxification, heavy metals can only be removed via the liver, kidneys, and bowels. The liver is the primary organ of detoxification and works in several ways. The liver filters large toxin particles from the blood, produces and releases bile (full of cholesterol and fat-soluble toxins), and denatures chemicals through a two phase detoxification process. In Phase I, toxins are either neutralized or they are converted into a form that can be neutralized in Phase II by a variety of enzymes.
While the body has several routes of detoxification, heavy metals can only be removed via the liver, kidneys, and bowels. The liver is the primary organ of detoxification and works in several ways. The liver filters large toxin particles from the blood, produces and releases bile (full of cholesterol and fat-soluble toxins), and denatures chemicals through a two phase detoxification process. In Phase I, toxins are either neutralized or they are converted into a form that can be neutralized in Phase II by a variety of enzymes.
Both Phase I and Phase II detox require several different nutrients, but the most important nutrient is glutathione, a major antioxidant. Getting enough glutathione is critical to the detoxification process and a deficiency in the nutrient has been linked to not just heavy metal poisoning, but also to various neurological and autoimmune conditions such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, multiple sclerosis, chronic fatigue, cancer, diabetes, HIV, autism, and epilepsy.
The process of detoxification produces a great deal of free radicals, which pose their own problems. The body then neutralizes these free radicals with antioxidant enzymes, primarily GST (glutathione-S-transferase), GPOX (glutathione peroxidase), and SOD (superoxide dismutase). These antioxidants are endogenous, that is, they are produced in the body, and made from glutathione and selenium. In locations with high levels of environmental toxic metals, the average person has lower than normal blood levels of these enzymes.
Producing these antioxidant enzymes begins with getting the right nutrients in the diet, specifically glutathione and selenium. Glutathione is a protein that can be found in several foods, especially asparagus, avocado, walnuts, and raw goat milk. Getting enough selenium can be tricky, as it depends on the quality of the soil in which food is grown. Brazil nuts are one of the best sources of selenium. Other sources of selenium include: fish, shellfish, meat, poultry, eggs, grains, sunflower seeds, grains, mushrooms, and onions.
It’s also possible to produce glutathione in the body, provided the right precursors are present. Compounds that can be used to produce glutathione in the body include folic acid, vitamin B12, and vitamin B6. It is however, far easier to simply take glutathione supplementation if the body can tolerate.
Glutathione is comprised of three sulphur-based amino acids, specifically glutamate, cysteine, and glycine. Eating foods high in sulphur, such as raw eggs and alliums (onions, garlic, and related vegetables), can also help boost glutathione levels.
 Chelation therapy calls for the use of chelating agents to bind with heavy metals so they can be more easily removed. One of the best nutritional chelating agents is Alpha Lipoic Acid, more commonly known as ALA. ALA is highly effective at binding with toxic metals, including mercury, cadmium, lead, arsenic, copper, and iron. Once ALA binds with these toxic metals, it neutralizes them so they can then be excreted from the body.
Chelation therapy calls for the use of chelating agents to bind with heavy metals so they can be more easily removed. One of the best nutritional chelating agents is Alpha Lipoic Acid, more commonly known as ALA. ALA is highly effective at binding with toxic metals, including mercury, cadmium, lead, arsenic, copper, and iron. Once ALA binds with these toxic metals, it neutralizes them so they can then be excreted from the body.
ALA neutralizes free radicals inside and outside the cells and is soluble in both fat and water. ALA can also be used to produce other antioxidants, including glutathione and vitamin C and E. Good sources of ALA include dark leafy greens and animal foods, particularly organ meats.
Good nutrition, especially adequate mineral intake, can help prevent the accumulation of heavy metals in the body. A diet deficient in calcium, for example, is associated with both increased lead absorption and decreased iron absorption. Other minerals that can protect against toxic metal absorption include magnesium, zinc, and selenium. To put it simply, there is an inverse relationship between toxic metals and essential minerals in the body. Eating a diet high in iron, calcium, zinc, and magnesium can help prevent absorption of toxic metals.
One of the best sources of iron is liver. Other good sources include red meat, fish, beans, figs, eggs, and leafy greens. Vitamin C improves iron absorption, so be sure to eat iron rich foods with foods high in vitamin C such as citrus fruits, tomatoes, berries, and melons. Cooking in cast iron cookware, especially with acidic foods like tomato sauces, is a great way to get more iron.
Dairy foods like cheese and yogurt are good sources of calcium, as are tahini and seaweeds.
Some of the best sources of zinc include spinach, mushrooms, and calf liver. Other good sources include sea veggies, pumpkin seeds, sesame seeds, meats like beef and lamb, veggies like asparagus, broccoli, and peas, shrimp, maple syrup, and several herbs, including basil, thyme, and mustard greens.
The best sources of magnesium include legumes, seeds, leafy greens and whole grains. Magnesium can also be obtained through the skin by rubbing with magnesium oil or other topical products.
In addition to ensuring you get enough of the proper nutrients in your diet, there are also certain key lifestyle changes you can make to reduce your chances of heavy metal poisoning, and help keep heavy metals from your environment and body.
Fasting increases absorption of toxic metals. Eating regular, nutritious meals, especially breakfast, can lessen absorption and reduce the risk of heavy metal poisoning.
While mercury-based thimerosal has been removed from many vaccines, and exists only in trace amounts in others, this does not make them safe. Even trace amounts of mercury are toxic, and where mercury has been removed, it’s been replaced by aluminum, which is also toxic. To make matters worse, by being injected directly into the muscle, the toxic ingredients in vaccines bypass the protective digestive tract. The minute amounts of metals are said to be “safe in small amounts”. However, many chronic health conditions, including allergies, asthma, and autism are on the rise. Rates of these conditions are highest in locations where environmental toxic metals are most concentrated.
Fiber binds with heavy metals and improves bowel function to remove these toxins from the body. Pectin is a type of soluble fiber that is especially effective and can be found in apples, pears, psyllium husk, slippery elm, legumes, and grains.
Skipping meals can increase absorption of heavy metals, but therapeutic fasting utilizing enzyme-rich juice can help the body release and excrete accumulated toxic metals.
Bottled water is a disaster, both for the environment and for your health. A good gravity fed water filter can remove most toxins, including heavy metals.
Heavy metal poisoning is one of the most common health conditions, simply because we seem to be surrounded by toxic metals in just about everything we do, and because they are so difficult to remove once they are in the body. Certain precautions can help, such as avoiding products that may contain toxic metals, and using water and air filters.
Good nutrition is especially vital, both in preventing metal toxicity and removing toxic metals from the body. Avoiding nutrient deficiencies will stop the body from using toxic metals in place of necessary vitamins and minerals. This will also support the body’s efforts to remove toxic metals that have built up.
 Gradually removing toxic metals from the body will help ease symptoms of adrenal fatigue by reducing toxic load on the glands and promoting the detoxification pathway in the NEM stress response system. However, caution is advised, as removing toxins too rapidly can overload the systems of elimination, leading to worsening of symptoms and potentially adrenal crash. It is therefore important to find an experienced doctor who will not jump into a detoxification program without evaluating the whole body and the root cause of your symptoms.
Gradually removing toxic metals from the body will help ease symptoms of adrenal fatigue by reducing toxic load on the glands and promoting the detoxification pathway in the NEM stress response system. However, caution is advised, as removing toxins too rapidly can overload the systems of elimination, leading to worsening of symptoms and potentially adrenal crash. It is therefore important to find an experienced doctor who will not jump into a detoxification program without evaluating the whole body and the root cause of your symptoms.
Self-navigation is highly discouraged for those with AFS. Improper detoxification is one of the most common causes of recovery failure, relapses, and adrenal crashes. Doing the right thing at the wrong time can weaken the body. Many are so carried away with the benefits that they do not carefully examine the body’s state each step along the way. Those with AFS and those suffering from serious heavy metal poisoning already have significantly weakened systems, and success is not guaranteed. In this case it’s important to consult with a qualified professional.
However, by taking steps towards better nutrition, cleaner air and water, and reducing or eliminating heavy-metal-containing products in the home, you can improve your chances of avoiding and detoxing from heavy metal poisoning.