 Oxygen therapy is definitely not a new concept. It simply involves supplementing oxygen to individuals that need it. However, IV oxygen therapy is not as common or straightforward as other oxygen therapy techniques. The very idea of injecting oxygen, a gas, into the blood goes against several medical laws, posing the risk of embolism. So why is IV oxygen therapy practiced today, and how safe is it really? Let’s find out.
Oxygen therapy is definitely not a new concept. It simply involves supplementing oxygen to individuals that need it. However, IV oxygen therapy is not as common or straightforward as other oxygen therapy techniques. The very idea of injecting oxygen, a gas, into the blood goes against several medical laws, posing the risk of embolism. So why is IV oxygen therapy practiced today, and how safe is it really? Let’s find out.
To understand IV oxygen therapy (IOT), let’s first consider what oxygen therapy is. In simple terms, oxygen therapy is the provision of supplemental oxygen to help people that cannot get enough of the oxygen their body needs. This therapy is common among people with respiratory conditions like COVID-19, sleep apnea, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
There are several oxygen therapy techniques. Usually, oxygen is delivered through a canula, face mask, or tubes surgically placed in the trachea. The oxygen involved here is delivered to the lungs. Conversely, IV oxygen therapy involves the intravenous administration of very small amounts of oxygen at a low infusion rate over a set period. This therapy is also called oxyvenation.
Unlike other oxygen therapy techniques, IV oxygen therapy is not done just to increase the oxygen saturation level. Instead, many health practitioners administer oxygen intravenously to stimulate eosinophilia, which involves stimulating increased levels of eosinophils, a type of white blood cell that fights disease. This is important in managing multiple health conditions. In addition, oxygen therapy can also help strengthen the body’s antioxidant mechanisms.
However, IV oxygen therapy requires several sessions to be effective, as a single administration will not have any significant effect.
Administering gas directly into the bloodstream poses a lot of health risks, particularly air embolism. This condition arises when a blood vessel is blocked by gas bubbles. Air embolism can be severe and potentially fatal, causing conditions like stroke and heart attacks. Another health risk is gas bubbles entering the central nervous system (CNS) and the brain, which can also be fatal. How, then, does IOT work?
During IV oxygen therapy, very small amounts of oxygen are administered at a low rate. Only about 2 percent of the administered oxygen dissolves in the blood. Of the remaining proportion, most oxygen molecules bind to the hemoglobin in red blood cells. The remaining undissolved administered oxygen is present in the blood as small bubbles.
The body then coats the oxygen bubbles with extracellular matrix-derived substances, usually fibronectin and fibrinogen, in a process called opsonization. This process allows the immune system to recognize the bubbles as foreign substances and prepare for their elimination. For the body’s defense response to these marked allergens, eosinophils need to be produced. The production of eosinophils is known as eosinophilia.
Studies have observed the absence of eosinophilia with other oxygen therapy techniques, explaining why IOT is the only oxygen therapy technique used for increasing eosinophils in the blood. Most of the health benefits of intravenous oxygen therapy are linked to its ability to stimulate eosinophilia.
Aside from eosinophils, some other biological substances, especially prostacyclin and paraoxonase-1, are produced due to the IV oxygen therapy mechanism of action. Prostacyclin is a major thrombocyte aggregation inhibitor, stimulating blood circulation and promoting vasodilation. These substances also contribute to the health benefits of the technique.
 For the administration of intravenous oxygen, patients have to be in a recumbent position with the head slightly elevated. However, patients cannot lie on their side. Even after administration, patients need to remain in lying down to reduce side effects.
For the administration of intravenous oxygen, patients have to be in a recumbent position with the head slightly elevated. However, patients cannot lie on their side. Even after administration, patients need to remain in lying down to reduce side effects.
The dosing of IV oxygen therapy is stated in terms of the amount administered and the infusion rate. For women, the starting dose is 10 ml, while it starts at 15 ml for men. However, after the initial dose, there are 2 ml incremental increases up to 40 ml for women and 50 ml for men. Each session usually lasts between 45 and 60 minutes.
The number of sessions of IOT a patient needs varies. Health practitioners often handle cases individually to determine the optimal dosing regimen. Usually, health practitioners administer intravenous oxygen two to three times a week to start. However, your ability to tolerate oxygen increases with time, and the dosing amount and frequency may increase to five times a week.
Intravenous oxygen therapy has been researched heavily over the last few decades. Below are some of the identified benefits of the therapy.
Inflammation in itself is not a bad thing, as it helps the body fight off foreign invaders and heal injuries. However, if inflammation lasts for prolonged periods, it is known as chronic inflammation and can be detrimental to health.
There are many causes of inflammation, including stress. The body has a natural mechanism for coping with stress known as the NeuroEndoMetabolic (NEM) Stress Response. The NEM system comprises several organs and systems in the body and is divided into six circuits. The inflammation circuit is responsible for managing inflammation in the body.
If the inflammation circuit dysregulates and chronic inflammation arises, multiple health problems could arise, including Adrenal Fatigue Syndrome (AFS). Adrenal fatigue is a syndrome where the body’s stress response cannot cope with life’s chronic stressors.
Chronic inflammation increases oxidative stress, producing a lot of free radicals, which in turn produce more inflammation. This is why it is important to address stress while managing these chronic inflammatory conditions.
While IOT is renowned for its role in eosinophilia, it also stimulates certain antioxidative enzymes, like paraoxonase-1 and glutathione peroxidase, which helps manage chronic allergic conditions. The reduction of eosinophils in the tissues after intravenous oxygen therapy has also been found to contribute to the therapy’s efficacy in chronic allergic inflammatory conditions like eczema, hay fever, psoriasis, and neurodermatitis. The eosinophils go from the tissues to the blood to get excreted, that's why you might have less allergic and inflammation response in your tissues.
IV oxygen therapy can also help manage chronic inflammatory gastrointestinal conditions like Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis.
Intravenous oxygen therapy is based on the principle of hormesis. Essentially, this principle states that environmental factors that can be toxic or lethal in high doses can be beneficial in low doses.
Administering high amounts of oxygen intravenously can certainly be detrimental to health and potentially fatal. However, temporary and repeated sub-toxic doses of intravenously administered oxygen can strengthen the body’s antioxidant mechanisms. This then increases the body’s capacity to prevent oxidative stress.
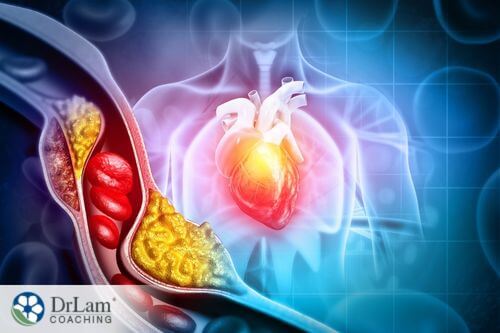 Atherosclerosis is the thickening and narrowing of the inner lining of the artery due to the build-up of fats, cholesterol, and other substances (known as plaque) in and on the artery wall. This condition itself often has no symptoms until the plaque ruptures or blocks blood flow.
Atherosclerosis is the thickening and narrowing of the inner lining of the artery due to the build-up of fats, cholesterol, and other substances (known as plaque) in and on the artery wall. This condition itself often has no symptoms until the plaque ruptures or blocks blood flow.
Also known as atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, this condition can cause other heart and health conditions, including heart attacks, stroke, aneurysms, and blood clots. Another condition that can promote these heart conditions is adrenal fatigue. The NEM circuit responsible for the regulation of blood circulation is the Cardionomic circuit.
Considering the inherent risk of the oxygen bubbles blocking the blood vessels, it may appear absurd to imagine that IV oxygen therapy can have any benefits for patients with atherosclerosis and related conditions. However, IOT has been found to have vasodilatory and anti-thrombotic effects, which can help in the management of atherosclerosis-mediated conditions.
IV oxygen therapy can be important in the management of several eye disorders, including glaucoma, retinal vein thrombosis, dry macular degeneration, macular edema, central serous retinopathy, retinitis pigmentosa, vascular optic atrophy, and hypertension with ischaemic papillary edema.
Aside from the role intravenous oxygen therapy plays in the management of these conditions, clinical trials also showed the therapy helped improve performance in vision and even better sleep.
Autoimmune conditions occur when the body attacks itself. Here, the immune system marks healthy body cells as allergens and attacks them. This can cause severe damage to tissues and organs. Medical experts have drawn a link between the opsonized oxygen bubbles from IOT and antigenic parasite antigens that also cause the proliferation of eosinophils.
Regarding autoimmune conditions, it is reported that the immune system attacks the opsonized oxygen bubbles and ignores the harmless endogenous antigens that would otherwise cause autoimmune conditions if attacked by the immune system. This could reduce the severity of autoimmune symptoms.
Some autoimmune disorders that IV oxygen therapy can be used to manage include multiple sclerosis, some types of narcolepsy, rheumatoid arthritis, and systemic sclerosis.
Recent studies confirm that IOT therapy may be helpful in liver conditions like chronic hepatitis and cirrhosis. The use of IOT for these conditions is informed by the therapy’s anti-inflammatory, antioxidative, antifibrotic, immunosuppressive, and vasodilatory prostacyclin properties.
As useful as intravenous oxygen therapy may be in managing multiple acute conditions, it is contraindicated in acute conditions requiring immediate medical attention. These include severe asthma attacks, acute heart attacks, pneumonia, and trauma.
While administering IOT, it is critical to restrict the gas bubbles to a small volume of blood. Therefore, individuals with heart septum defects cannot safely get the therapy, considering the high risk of the microbubbles entering general circulation. This also applies to individuals with patent foramen ovale, which describes an opening between the heart’s upper right and left chambers.
Smoking is also contraindicated for IV oxygen therapy. This is because the carbon monoxide inhaled while smoking has a far higher affinity for hemoglobin than oxygen. Therefore, there is a high probability that the administered oxygen will remain longer as bubbles in the blood. Furthermore, smoking is often associated with lower prostacyclin production, which may interfere with the therapy.
While smokers can benefit from IV oxygen therapy, their tolerance levels are much lower than non-smokers, and many health practitioners are wary of administering the therapy. Those with lung diseases also have to start at a much lower dose of IV oxygen therapy.
 Below are some of the side effects that may result from IOT. They include:
Below are some of the side effects that may result from IOT. They include:
Administering oxygen intravenously, like other intravenous gas administration techniques, is risky. Since 1978, medical oxygen has been approved only for respiratory use, with many health organizations ignoring IV oxygen therapy. This is primarily because of the high risk of air embolism, which can be potentially fatal.
However, medical practitioners can prevent this by administering small air bubbles over an extended period. Studies show that the smaller the needle used for administration, the smaller the bubbles produced in the bloodstream.
Also, it is critical that you only have this procedure done at reputable facilities. Administering anything of less quality than medical-grade molecular oxygen further increases the risk of embolism. Some medical experts have also suspected that the eosinophil proliferation IOT induces may be detrimental to health if it leaves the blood. However, clinical trials show that the eosinophil granulocytes produced are retained in the blood, as that is where the allergens are.
IV oxygen therapy is a technique that involves the administration of oxygen intravenously. The aim is usually to stimulate eosinophilia and prostacyclin production, which are useful in the management of many conditions. Particularly, intravenous oxygen therapy helps boost the antioxidant defense mechanisms of the body, as well as manage many chronic inflammatory conditions.
While the therapy can have many health benefits, it can also be fatal if not handled properly. As such, only reputable and experienced medical practitioners should be considered for IV oxygen therapy.
For more information about IV oxygen therapy, the team at Dr. Lam Coaching can help. We offer a free, no-obligation phone consultation at +1 (626) 571-1234 where we will privately discuss your symptoms and various options. You can also send us a question through our Ask The Doctor system by clicking here.
There is no fixed amount on the number of IOT sessions a person needs. While health experts often advise up to five treatment sessions a week, some people may only tolerate two to three sessions weekly. With more sessions, oxygen tolerance increases, causing the dosing amount and frequency to increase.
