Infertility affects both men and women and prevents many couples from starting a family. There are several reasons for female infertility, from structural problems in the reproductive system to endometriosis. However, a fertility test can provide answers that have the potential to help solve infertility issues. Here you learn about the causes of female infertility and the different tests and procedures for testing fertility.
 Infertility is the inability of a couple to conceive even after frequent, unprotected sexual intercourse for a year. Couples can also experience subfertility and fecundity. Subfertility can involve taking twelve or more months to conceive. Fecundity is difficulty in staying pregnant or carrying a baby to term.
Infertility is the inability of a couple to conceive even after frequent, unprotected sexual intercourse for a year. Couples can also experience subfertility and fecundity. Subfertility can involve taking twelve or more months to conceive. Fecundity is difficulty in staying pregnant or carrying a baby to term.
Infertility affects roughly 15% of all couples in the United States and one in six couples under 35 years of age. Many couples over 35 also have problems becoming pregnant. The problem can rest with the male, the female, or both partners. This is where a fertility test can help to determine the cause of infertility.
Several things could go wrong that could cause female infertility. Four common problems according to the National Institutes of Health include:
A woman who has problems with her menstrual cycle may have infertility problems. The average menstrual cycle lasts 28 days. During the cycle, hormonal changes control the release of the egg from the ovary and prepare the uterine lining for the implantation of an embryo. Furthermore, an abnormal menstrual cycle or menstrual disorders could indicate infertility. This could be due to polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or uterine fibroids.
Structural uterine problems may interfere with the implantation of the embryo. Several structural issues that may cause infertility include:
An infection could be the reason for infertility in a man or woman. In women, untreated gonorrhea and chlamydia can lead to pelvic inflammatory disease. This may lead to scarring that creates a blockage in the fallopian tubes. Furthermore, chronic infections in the cervix and surgical correction of HPV-related cervical lesions can minimize the quantity or quality of cervical mucus. This can make it challenging for a woman to get pregnant.
Eggs may fail to reach maturation for one reason or another. Factors that can impact this process include PCOS, obesity, and the absence of specific proteins critical for the egg to mature, among other possible reasons. An immature egg may fail to release at the appropriate time, may fail to travel down the fallopian tubes, or may fail to fertilize.
Signs of infertility in women may vary from one woman to the next. The most common sign of infertility in women is having trouble conceiving. Depending on the cause of infertility, a woman may also experience symptoms such as:
 Pelvic pain
Pelvic painIf you notice these or any unusual symptoms, discuss them with your physician. Sometimes, symptoms can be an indication of underlying hormonal conditions. A fertility test can shed light on hormonal issues that your physician may need to address.
Your hormones regulate various functions in your body. The Hormone Circuit of the NeuroEndoMetabolic (NEM) Stress Response is important in this process. It comprises the adrenal glands, reproductive organs, and the thyroid glands. These organs are active in processes in the body, like metabolism, energy production, and reproduction.
Also, the NEM Stress Response plays a vital role in how your body responds to stress. Stress can impact hormonal balance and by extension, reproductive health.
Consequently, hormone imbalance can impact these bodily functions and cause health problems. Chronic stress can develop as a result and cause fatigue in the adrenal glands. This prevents them from producing an adequate amount of natural hormones, such as cortisol. Stress has the potential to affect fertility. Chronic stress can lead to adrenal fatigue, a condition that can contribute to infertility. Adrenal Fatigue Syndrome (AFS) is the non-Addison's form of adrenal dysfunction, where the body's stress response cannot keep up with life's chronic stressors. As such, it’s critical that the Hormone Circuit remains in a state of balance.
If a couple finds that they have been unsuccessful at pregnancy after a year, both should get a thorough physical and medical assessment. The woman should immediately get a fertility test and the man a semen analysis. Both must get a checkup for possible infertility issues, since it’s not solely a female concern.
Semen analysis is a laboratory test that assesses male fertility. An assessment of male infertility begins with a thorough medical and sexual history and a comprehensive physical examination. That is usually followed by a semen analysis. The specialist will evaluate the semen by looking at a variety of factors. These include the total number of spermatozoa, fluid volume, sperm concentration, and the nature, viability, motility, shape, and secretion composition of the spermatozoa.
The specimen usually involves a semen sample collection by the man. Specifically, a man performs self-masturbation close to the laboratory or at home.
Based on the 2010 WHO laboratory manual for the examination and processing of human semen, semen analysis involves the following steps:
This fertility test can be relatively labor-intensive and also complex, but necessary for accurate and reliable results.
Fertility test can involve blood test that falls under the category of hormone test. They can check for the following:
 Anti-mullerian hormone (AMH): A physician may recommend a blood test to determine AMH levels in a woman’s body. AMH reserve is the most popular assessment in the fertility world. Normal AMH level ranges 1.06 - 6.9., with optimal levels 2 - 4, while <1 amounts to low reserves and poor IVF response.
Anti-mullerian hormone (AMH): A physician may recommend a blood test to determine AMH levels in a woman’s body. AMH reserve is the most popular assessment in the fertility world. Normal AMH level ranges 1.06 - 6.9., with optimal levels 2 - 4, while <1 amounts to low reserves and poor IVF response.
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH): This particular hormone stimulates the fertile growth of the follicle containing the egg. A low level of FSH could cause amenorrhoea, where a female is not having periods at all
Luteinizing hormone (LH): Just before ovulation, LH plays a key role in stimulating the rapid growth of the follicle containing the fertile egg. This hormone may be normal or at elevated levels in females with irregular or no periods. Also, it may be normal or low in females with no periods. Furthermore, it may be significantly low in females who have experienced excessive weight loss which creates a health risk for them.
Prolactin (PRL): During pregnancy, PRL is usually elevated and critical for breastfeeding. However, this hormone can be elevated in females who are not pregnant, but whose periods have stopped or are infrequent. Such an issue could arise from developing a small tumor in the pituitary gland or taking specific medications.
Thyrotrophin (TSH): A check of TSH level can help to determine if the thyroid gland is underactive. There’s a connection between an underactive thyroid gland and irregular periods.
Androgens: Elevated levels of the hormone androgen in females have been linked to ovulation problems and polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS).
While semen tests and blood tests are the most common forms of fertility tests, some other tests and procedures are also used for testing fertility. A fertility specialist determines which fertility test is best for your unique situation. Other tests include:
To check ovulation, your physician may recommend that you start charting your basal body temperature. However, while BBT charting has long been used for this purpose, experts doubt its reliability as an accurate technique when compared to other types of ovulation tests.
The postcoital test involves a woman first having sexual intercourse several hours in advance. Then, the woman visits her physician's office, where she provides a sample of cervical mucus. This is taken for microscopic examination. In this process, both the viability of the sperm and their interaction with the cervical mucus are tested. Essentially, it can help to determine if the sperm can penetrate and survive in the cervical mucus.
An ultrasound can check the condition of a woman’s ovaries and uterus. In doing so, a healthcare provider can use this exam to determine whether the follicles in the ovaries are functioning normally. As such, this form of fertility test is usually done 15 days before a female's expected menstrual period.
A hysterosalpingogram, also referred to as an HSG or "tubogram,” is a procedure in which a series of X-rays is taken of a female’s fallopian tubes. It’s typically performed after a liquid dye has been injected into the female’s uterus via the cervix and vagina. Also, an HSG is beneficial in determining the existence of fallopian tube blockages and uterine defects in a female. Typically, this procedure is performed between days six and 13 of a female’s cycle.
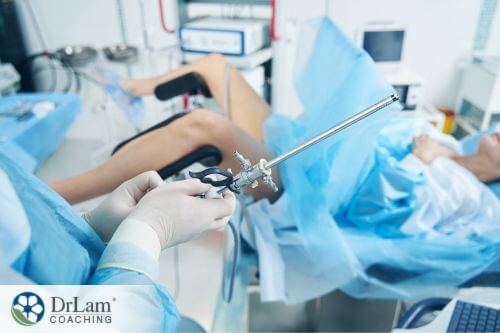 In the instance that an issue or abnormalities were discovered by a hysterosalpingogram (HSG), the physician might order a hysteroscopy. During this procedure, a thin telescope-like instrument is inserted through the cervix into the uterus. In practice, this allows the physician to view and photograph the area to see any abnormalities, growths, or scarring in the uterus.
In the instance that an issue or abnormalities were discovered by a hysterosalpingogram (HSG), the physician might order a hysteroscopy. During this procedure, a thin telescope-like instrument is inserted through the cervix into the uterus. In practice, this allows the physician to view and photograph the area to see any abnormalities, growths, or scarring in the uterus.
After a hysteroscopy has been performed, a physician may also order a laparoscopy. This procedure involves the insertion of a laparoscope into the abdomen via a small incision. It provides a view of the fallopian tubes, ovaries, and uterus. Additionally, the presence of issues like endometriosis and scarring can be identified. Typically, a laparoscopic procedure requires general anesthesia.
A physician may order a biopsy of a woman’s uterine lining to see if everything is normal to support embryo implantation and growth. This helps determine if the lining of the uterus is thick enough to support this. For this fertility test, a fertility specialist scrapes a small sample of tissue from the endometrium just before menstruation. Then, the sample is analyzed in the lab.
A premarital fertility checkup or screening can be an essential part of family planning for some couples. This check-up involves a couple who intends to get married and have kids. Essentially, this is similar to routine health screenings, but with additional tests meant to:
Additionally, a fertility test before marriage is important for couples to be aware of health issues of which they may not have been aware. It allows them to take necessary action toward successful family planning.
The experts recommend that you get an infertility evaluation if you have failed to get pregnant after a year of having regular sexual intercourse without using birth control or donor insemination. Some physicians may recommend infertility testing if you haven’t conceived after six months of trying.
Furthermore, several instances that warrant seeing your physician about a fertility test include a history of:
You may be able to address your infertility issues with the right support measures taken to boost fertility. You want to tackle the four Rs, as one fertility expert calls them -- reveal, remove, rebalance, and receive.
A physician could introduce supplements to restore balance to the body and boost fertility in both men and women. Different supplements can provide different benefits. Some of the best supplements that can help include:
 White Peony and Licorice: This is an essential PCOS formula. It also improves LH and FSH ratios and reduces testosterone in women.
White Peony and Licorice: This is an essential PCOS formula. It also improves LH and FSH ratios and reduces testosterone in women.Also, check out Dr. Lam’s P-Balance Cream which can help to restore your hormonal balance by boosting progesterone levels safely and naturally. Specifically, progesterone causes the uterine lining to thicken, helping to create an ideal support environment in the uterus for an embryo to implant itself.
It may be worth getting a fertility test depending on your personal situation. The following are some of the reasons it’s worthwhile:
At-home fertility tests are available on the market, which allows you to perform a self-test for evaluation. However, these tests don’t always present the most accurate results, and they are limited in determining all the causes of infertility.
It’s often best to consult a healthcare provider to have expert support and get the right tests based on your symptoms or need.
A fertility test can help couples not only plan for their future family but also identify and remedy any issues that could impact their ability to get pregnant. If you are having difficulty getting pregnant, consult with a healthcare provider. A proper assessment can provide an accurate determination of the reason for this challenge. Visit your doctor to know if your symptoms are an indication of infertility.
If you would like to learn about natural ways to remedy your symptoms, the team at Dr. Lam Coaching can help. We offer a free** no-obligation phone consultation at +1 (626) 571-1234 where we will privately discuss your health concerns and various options. You can also send us a question through our Ask The Doctor system by clicking here.

P-Balance Cream: Unlock Your Natural Fertility Potential!
Carson, Sandra Ann, and Amanda N Kallen. “Diagnosis and Management of Infertility: A Review.” JAMA vol. 326,1 (2021): 65-76. doi:10.1001/jama.2021.4788 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34228062/
Leslie SW, Soon-Sutton TL, Khan MAB. Male Infertility. [Updated 2023 Mar 3]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK562258/
Office of Communications. What are some possible causes of female infertility? National Institutes of Health. https://www.nichd.nih.gov/health/topics/infertility/conditioninfo/causes/causes-female
Sunder M, Leslie SW. Semen Analysis. [Updated 2022 Oct 24]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK564369/
Four main causes of infertility in women include reproductive system problems, menstrual problems, eggs not maturing, and infection. Several fertility tests, such as hormone testing or ovulation testing, can help to determine fertility. However, the man should also be tested, and a doctor is best able to recommend the best tests for you.