 Food allergy, food sensitivity, and food intolerance are all a form of reaction to ingested food, but their causes differ, and so should how you address them. These conditions may have symptoms that mirror each other, so they are often mistaken for each other. It’s important to be able to tell them apart in order to make the right choices about food-related issues. Here's how to spot the difference between food allergy vs food intolerance.
Food allergy, food sensitivity, and food intolerance are all a form of reaction to ingested food, but their causes differ, and so should how you address them. These conditions may have symptoms that mirror each other, so they are often mistaken for each other. It’s important to be able to tell them apart in order to make the right choices about food-related issues. Here's how to spot the difference between food allergy vs food intolerance.
A food allergy occurs when your body triggers an abnormal immune response to certain foods that are ingested. The body goes into protective mode against the perceived threat when this happens.
A food allergy is caused by allergens, or proteins, that travel through the body. They can accumulate in different areas, such as the throat, GI tract, or skin, where they cause symptoms.
In some food allergies, your immune system recognizes these allergens as invaders and releases immunoglobulin E (IgE), protein antibodies. The next time you eat that food, your mast cells, part of your immune system, are triggered by the presence of IgE to release histamine, causing an allergic reaction and familiar symptoms like sneezing or hives.
Other allergies are not mediated by IgE, and these allergies can take longer to manifest, although they still involve an abnormal immune response to food and the release of histamine. Scientists are still working to identify the primary mediating factors in these cases. Likewise, there are not good laboratory tests for these other types of allergies, meaning that a food elimination challenge may be the best method to identify them.
An allergic response can occur within a few minutes, a few hours, or a few days, regardless of the amount of the trigger food ingested. In the case of IgE-mediated allergies, a severe response could mean a life-threatening reaction - anaphylaxis - in which the airways tighten and blood pressure can drop quickly.
Food allergies are generally categorized into three types. These are:
 When food intolerance occurs, your digestive system experiences difficulty digesting or breaking down a particular food. A food intolerance typically affects only the digestive system, for example, lactose intolerance or gluten intolerance. The immune system is not responsible for food intolerance. Individuals with food intolerances tend not to make an adequate amount of a specific enzyme needed by the digestive system to fully break down a certain food or food ingredient.
When food intolerance occurs, your digestive system experiences difficulty digesting or breaking down a particular food. A food intolerance typically affects only the digestive system, for example, lactose intolerance or gluten intolerance. The immune system is not responsible for food intolerance. Individuals with food intolerances tend not to make an adequate amount of a specific enzyme needed by the digestive system to fully break down a certain food or food ingredient.
Also, with some food intolerances, you may still be able to eat small quantities of the offending food without any reaction. Someone with certain gastrointestinal conditions may be more susceptible to food intolerance. And while food intolerance tends to be a life-long issue, it is not acutely life-threatening.
In some scientific circles, it's believed that food sensitivity is a reaction to the ingestion of a particular food that may be linked to increased levels of certain IgG antibodies and not IgE antibodies. While IgG is a normal part of how the body responds to food antigens, this response may be more dramatic in some people.
Food sensitivity symptoms can be immediate or delayed for several days after ingesting the trigger food. They may be unpleasant, but are not typically urgent or require emergency care. Common symptoms include fatigue, brain fog, sneezing, runny nose, bloating, diarrhea, and migraines. It's possible for a person to have food sensitivities but go years without an awareness of it because of the delayed reaction times and often vague symptoms that mimic common ailments.
Regarding the symptoms of food allergy vs food intolerance, the two can be easily confused and one is mistaken for the other. However, there are also some differences.
Depending on the type of food allergy, symptoms can occur between a few minutes following exposure to a couple of days. Some of the symptoms of food allergy include:
Severe cases of food allergies can cause anaphylaxis, which could be fatal. This reaction needs urgent medical attention. Potentially life-threatening symptoms associated with anaphylaxis may include:
Those with severe allergies should carry an epipen, or epinephrine autoinjector, to help arrest this kind of reaction.
The symptoms of food intolerance aren’t life-threatening. Symptoms can appear within a few hours following ingestion of a trigger food and travel through the digestive tract. Some common symptoms to look out for include:
Comparing food allergy vs food intolerance, you find different types of allergens and offending intolerances.
 Roughly 90% of food allergic reactions are related to eggs, fish, peanuts, tree nuts, milk, wheat, and shellfish.
Roughly 90% of food allergic reactions are related to eggs, fish, peanuts, tree nuts, milk, wheat, and shellfish.
Other food allergens can include, soy, linseed, garlic, sesame seed, peach, avocado, kiwi fruit, celery, passion fruit, mustard seeds, and aniseed.
There are several common types of food intolerances. These include:
Where food sensitivities can be caused or worsened by a condition known as adrenal fatigue syndrome, which is caused by chronic stress. It results in the overuse of the NeuroEndoMetabolic (NEM) stress response, which causes cortisol levels to spike. This activates the Inflammation circuit, consisting of the microbiome, the immune system, and the GI tract. An overactive immune system can cause or worsen reactions to foods and other substances. Likewise, bacterial imbalances in the gut can lead to leaky gut, releasing food protiens into the body that can then be identified as threats by the immune system.
Fatigue and new food sensitivities are strong indicators of adrenal fatigue, and the slow onset of these symptoms is common for those experiencing the condition. Delayed food sensitivity, which is linked to adrenal sensitivity, causes particular bodily systems and functions to slow down. Food sensitivity symptoms can worsen when adrenal issues arise, like increased inflammation. Healing your adrenals, which can take some time, can help to reduce food sensitivities. So too can avoiding trigger foods like wheat or gluten.
It can be very difficult to identify whether a problem is due to a food allergy vs food intolerance. There are a number of tests that your doctor may order to check for a food allergy or an intolerance. Some of the best ones can be done at home yourself, but they do take discipline.
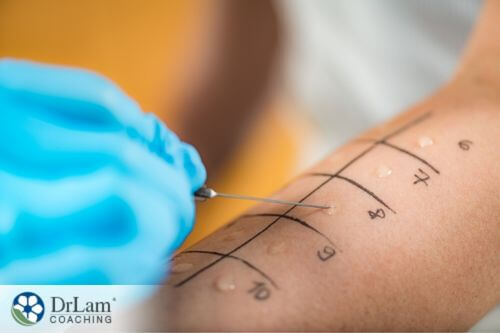
There is no cure for food allergies. In the world of food allergy vs. food intolerance, food allergies can be managed with strict avoidance of the foods that trigger an allergic reaction. The severity of your food allergy will help your doctor or allergist determine if you may need certain medications, like epinephrine auto-injectors. Some medications that a doctor may recommend include:
 Consult with a doctor or allergist if you suspect that you have a food allergy. Identifying and avoiding the allergen is often the best course of action.
Consult with a doctor or allergist if you suspect that you have a food allergy. Identifying and avoiding the allergen is often the best course of action.
You can also pay attention to food labels and product ingredients to avoid exposure to certain hidden allergens, like nuts, eggs, and sulfites. You may need to look up other names a food you are allergic to can appear as, as many foods are hidden in food labels. It’s a good idea to consult with a registered dietitian who can help you to maintain a nutrient-rich balanced diet, while safely avoiding foods that can trigger an allergic reaction.
If you are dealing with food intolerance, you may have to change your diet by reducing or eliminating foods your body does not tolerate. You may be able to limit symptoms by consuming small amounts of a problem food rather than eliminating it. Your doctor may recommend over-the-counter medicines, such as antacids or antidiarrheals (e.g. Imodium, Pepto-Bismol) to help manage some symptoms.
Lactose-free milk and other dairy products are available as an option for individuals who are lactose intolerant. Also, lactase enzyme, which helps to break down the lactose, can be found over-the-counter in the form of pills or drops. You can ingest a pill before consuming dairy products or add lactase drops directly to your milk products.
Restoring balance to the Inflammation circuit can also help to reduce the severity of food sensitivities. Taking Omega 3 or bromelain supplements, probiotics, and drinking lots of water may help, along with taking steps to reduce inflammation and improve gut health. If you experience adrenal fatigue, this could mean careful management of the ailment.
It's very important to heal the gut if you have food sensitivities as it could worsen in the future down the line to worse consequences like autoimmune disease or chronic fatigue or inflammation in the gut.
Call your doctor if you have an allergic food reaction and you experience a loss of consciousness, swelling of the lips, mouth, throat, or tongue, or trouble breathing. Also, get emergency care if you suffer an asthma attack after eating, or after an epinephrine shot, even if you feel better.
If you have a food intolerance issue, call your doctor if you experience extreme diarrhea or abdominal pain, a severe food reaction, or weight loss that's puzzling.
Whether it's a food allergy, food intolerance, or food sensitivity, it can compromise your overall health and well-being. However, knowing what food is the problem is often the key to managing the symptoms. If you suspect you have an allergy or intolerance to a food, try going on a food elimination diet and keeping a food diary. Then, schedule an appointment with an allergist to get tested. Often, knowing which foods trigger your symptoms is key to keeping them under control.
If you are concerned you have a food sensitivity or allergy, but aren't sure which, the team at Dr. Lam Coaching can help. We offer a free** no-obligation phone consultation at +1 (626) 571-1234 where we will privately discuss your symptoms and various options. You can also send us a question through our Ask The Doctor system by clicking here.
When it comes to a food allergy vs food intolerance, a food allergy occurs when your body triggers an abnormal immune response to certain foods that are ingested. On the other hand, a food intolerance occurs when your digestive system experiences difficulty digesting or breaking down a particular food because of the absence of a specific enzyme. Allergies can be a life-threatening emergency, while intolerances are generally not.
