 More than nine million cases of depression are diagnosed in the US alone. Depression is a serious mental health disorder that can majorly disrupt your daily life. Behavioral and physical symptoms include altered moods, loss of interest in daily activities, and changes in appetite. Most often, energy levels drop, sleep is elusive, and your self-esteem is diminished. At worst, depression is associated with suicidal tendencies. Statistics of this mental illness are alarming. Moreover, depression diagnoses are shown to have increased in all the states of America, with the exception of Hawaii. The rate of increase of depression in the US between 2013 and 2016 was 33%, with female teenagers and millennials being the most affected. So, what’s going on with the millennial generation? Why do they constitute such a large portion of those suffering from this horrible disease? Depression in millennials is a hot debate and highlights the need for major changes in current and future healthcare requirements.
More than nine million cases of depression are diagnosed in the US alone. Depression is a serious mental health disorder that can majorly disrupt your daily life. Behavioral and physical symptoms include altered moods, loss of interest in daily activities, and changes in appetite. Most often, energy levels drop, sleep is elusive, and your self-esteem is diminished. At worst, depression is associated with suicidal tendencies. Statistics of this mental illness are alarming. Moreover, depression diagnoses are shown to have increased in all the states of America, with the exception of Hawaii. The rate of increase of depression in the US between 2013 and 2016 was 33%, with female teenagers and millennials being the most affected. So, what’s going on with the millennial generation? Why do they constitute such a large portion of those suffering from this horrible disease? Depression in millennials is a hot debate and highlights the need for major changes in current and future healthcare requirements.
You may have heard the term “millennial” many times, but maybe you’re not quite sure what it truly means. First of all, millennial refers to anyone born between 1981 and 1996, the age group between 22 to 36 in the year 2018. Although the term is used rather broadly, the millennial generation have a few characteristics that set them apart:
The most recent study conducted by Blue Cross Blue Shield shows a 47% increase of depression in millennials. The group also was also shown to be 30% less healthy due to the fact that depression often causes chronic health conditions. Taking a closer look at this demographic, there are a few different reasons why depression may be so rampant. Young adults these days are facing a more competitive environment, unrealistic expectations, and different parenting styles than any generation before them. Some of the following reasons may be playing into the increased incidence of depression:

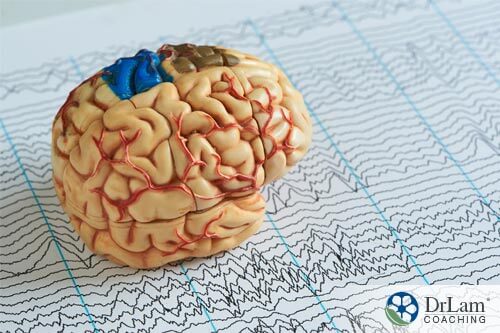
Along with the environmental circumstances that are associated depression in millennials, there are also physiological factors as well. Sufficient evidence now supports the idea that abnormal activity of neural circuits may play a major role in mental health conditions.
Neurotransmitters are the chemicals responsible for the communications that takes place throughout your entire body. Signals are sent from your brain via neurons to regulate your entire system and all of its functions, including physical and cognitive performance, pain tolerance, perception, weight gain and loss, sleep, and emotional wellbeing. Scientific research has revealed that disruption to any one part of this system is felt throughout your entire body.
It’s estimated that 80% of the population has some sort of chemical imbalance within their neurotransmitter system. Chemical imbalances are extremely common these days and are the root cause of many health conditions. When there is an imbalance, the body and mind cannot not communicate effectively, and depression may be one of the outcomes.
There are five main neurotransmitters responsible for triggering depression in millennials:
We all know how important a healthy diet is. Conclusive evidence now shows that a diet lacking in essential nutrients could be playing a major role in millennial depression. There is a causal link between what you eat and your risk of depression. In fact, nutrition is such an important part of mental health that there is now an entire field dedicated to the topic, called nutritional psychiatry. What we eat matters for every part of our body, but crucially our mental health. Some millennials are right in the middle of fast-paced careers, others are parenting, while still others may be searching for the right job or pushing through university, so nutrition may not be making it onto the list of high priorities.
A diet full of fruits and vegetables, olive oil, whole grains, fish and minimal quantities of animal meat along with low-fat dairy products is associated with a decreased risk of depression. In contrast, a diet characterized by refined grains, sugary foods, high-fat dairy products, high consumption of red and processed meat, as well as minimal amounts of fruits and vegetables, is now associated with an increased chance of developing depression.
 A number of factors contribute to the physical health and mental stability of millennials, as well as the rest of the population. Hormones play a major role in everything that happens in your body including hunger, energy levels, weight, sleep, and mood. If your adrenals are stressed, every cell in your body will be affected. Adrenal hormones are closely linked to cognitive function and altered cortisol levels due to an overly stressed body—regardless of whether they are too high or too low—have also been linked to anxiety and depression.
A number of factors contribute to the physical health and mental stability of millennials, as well as the rest of the population. Hormones play a major role in everything that happens in your body including hunger, energy levels, weight, sleep, and mood. If your adrenals are stressed, every cell in your body will be affected. Adrenal hormones are closely linked to cognitive function and altered cortisol levels due to an overly stressed body—regardless of whether they are too high or too low—have also been linked to anxiety and depression.
If you’re suffering from a preexisting condition like Adrenal Fatigue Syndrome (AFS), you’re more prone to experiencing depression, therefore it’s important to take every measure possible to ensure your environment is free of unnecessary stress and your nutrition is top-notch.
Depression should be taken very seriously and addressed immediately. If left unchecked, severely altered mood conditions like depression can lead to suicidal tendencies. If you or someone you love suffers from depression, it’s important to speak to a professional who can offer therapy, medication, and/or nutritional advice. Depression can also be the result of other serious medical conditions and should never be ignored.
Depression in millennials has been linked to many factors. There is some evidence indicating that social media could play a major role, however, there are many other factors that could contribute as well including nutrition and education, and even how you were parented.
