 Despite the great progress in science and technology, several chronic infections still remain untreated. Antibiotics tend to work initially, but often fail in the long run to get rid of these infections. Extensive research reveals that biofilm is a significant contributing factor. It is the underlying reason for people not feeling better even after being treated for chronic infections. However, there is evidence that natural botanicals can be helpful in effectively addressing the issue.
Despite the great progress in science and technology, several chronic infections still remain untreated. Antibiotics tend to work initially, but often fail in the long run to get rid of these infections. Extensive research reveals that biofilm is a significant contributing factor. It is the underlying reason for people not feeling better even after being treated for chronic infections. However, there is evidence that natural botanicals can be helpful in effectively addressing the issue.
Before we discuss the possible solutions, let’s explore the formation of these biofilm structures.
Microorganisms tend to move freely about as single cells referred to as planktonic forms. These individual microorganisms may then attach to a surface such as the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, clump together into a matrix form and develop a colony.
Biofilm is a densely packed colony of microorganisms enclosed in secreted extracellular polymeric substance (EPS) matrix. This matrix is like a slimy layer and acts as a glue. It also forms a physical barrier around the colonizing microorganism. In simple words, EPS is a protective shield which the microbes use to protect themselves from your immune system. This shield also hides the microorganisms, making it hard to detect them in lab tests and difficult to address.
Within this matrix, the microorganisms operate as a coordinated group similar to multicellular organisms. Larger colonies may have various species of microorganisms within their very complex structures. Furthermore, the protective shield makes the microorganism resistant to antibiotics and medications, which makes the infections chronic.
These pathogen colonies can grow on any surface. These include human, animal and plant tissues, medical devices and implants, contact lenses, industrial and household pipes. Whenever the environment is always wet, then this slimy layer can easily transport nutrients to help the microorganisms thrive and multiply.
Research reveals that these colonies of pathogens alone are responsible for up to eighty percent of the chronic infections and sixty-five percent of microbial infections in the human body. Biofilm can be found throughout the epithelial lining of the nasal passage and the GI tract. One of the common examples of biofilm is dental plaque, the slimy buildup on your teeth.
The microbial colony can also be present on wounds. This contains several bacteria including Klebsiella pneumoniae and staph aureus. Chronic wound infections are often the result of the presence of such films. Bacterial communities might not always demonstrate symptoms of infection, but they adversely affect healing.
There are several reasons why lab tests often fail to detect this colony of pathogens in your body:
The pathogens are enclosed in a slimy protective matrix shield. This means that cultures and swabs often show negative results. Stool tests may also prove inconclusive, as the samples do not contain any of these pathogens.
 It is difficult to obtain microbial film samples from some areas of your body. For example, it’s hard to get samples from the GI tract, as this would require invasive endoscope. Present procedures would also fail in removing the colonized bacteria hidden within the slimy layer of your GI tract.
It is difficult to obtain microbial film samples from some areas of your body. For example, it’s hard to get samples from the GI tract, as this would require invasive endoscope. Present procedures would also fail in removing the colonized bacteria hidden within the slimy layer of your GI tract.
Pathogens from these films are not easily cultured. The obtained sample might test negative, as the microbes can adapt to lower nutrient requirements.
Biofilm formation is classified into four stages:
This is the initial contact of the moving microorganisms with a surface. The microorganisms then start to form a monolayer and an extracellular matrix (or slime) for protection. The matrix comprises of structural proteins, extracellular polysaccharides, nucleic acid, and cell debris. These components are all referred to as extracellular polymeric substances (EPS). Extracellular DNA also plays a dominant role in the initial stage of matrix formation, and the structural proteins and polysaccharides help in the later stages.
During this stage, the microorganisms form a monolayer by growing into micro-colonies. They exhibit significant growth, as well as cell-to-cell communication known as quorum sensing.
The microbial colony now grows into a stronger three-dimensional structure where the attachments are irreversible.
During this stage, some of the matured microbial films begin to detach and disperse into the environment. These dispersed planktonic cells may potentially start a new cycle of biofilm colony formation.
Several types of bacteria and fungi can form these films. Regardless of the species, most bacteria (including aerobic and anaerobic types) exist in these films. Some of these bacteria include Staphylococcus epidermidis and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The microbial film of the GI tract often contains LPS Endotoxin from Gram-negative bacteria. Some other examples of bacteria that may be found in the biofilm include Candida tropicalis fungus, Escherichia coli, and Serratia marcescens bacteria.
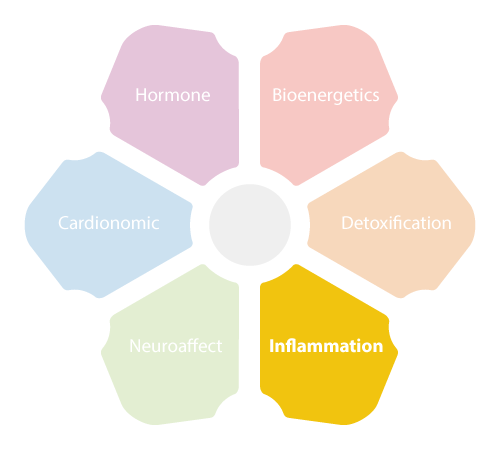 When colonies of pathogens grow in your body, they can trigger stress. The NeuroEndoMetabolic (NEM) Stress Response System helps your body deal with stress. It is an intricate network of various organs and six circuits. One of these circuits, the Inflammation Circuit, functions in close coordination with your adrenal glands to help your body deal with stress. The pair of walnut-shaped adrenal glands are located above your kidneys, and they produce the anti-stress hormone cortisol as a part of the response system.
When colonies of pathogens grow in your body, they can trigger stress. The NeuroEndoMetabolic (NEM) Stress Response System helps your body deal with stress. It is an intricate network of various organs and six circuits. One of these circuits, the Inflammation Circuit, functions in close coordination with your adrenal glands to help your body deal with stress. The pair of walnut-shaped adrenal glands are located above your kidneys, and they produce the anti-stress hormone cortisol as a part of the response system.
When your body experiences stressful conditions, the NEM signals your adrenal glands through the Hypothalamus-Pituitary-Adrenal (HPA) axis for secreting cortisol to deal with stress. However, when stress persists, the adrenal glands are forced to secrete more cortisol. This exerts additional pressure and overburdens them. Therefore, the adrenal glands are no longer able to secrete adequate cortisol. This reduces your body’s natural stress-fighting ability, and can lead to adrenal fatigue.
Adrenal Fatigue Syndrome (AFS) occurs when you frequently experience extreme stress along with some other symptoms. These include anxiety, brain fog, insomnia, low energy levels, difficulty in waking up, low concentration levels, stubborn weight gain, and craving for fatty and salty foods.
The Inflammation Circuit of the NEM comprises of the gut, microbiome and immune system. Any imbalance of this circuit can lead to food and chemical sensitivities, recurrent illness with a prolonged healing period, leaky gut, musculoskeletal pain, exacerbation of autoimmune disorders, and yeast infections.
Biofilms are found almost everywhere and may significantly impact human health in both positive and negative aspects. For example, Staphylococcus epidermidis bacteria produce a positive effect by impeding the colonization of potentially pathogenic bacteria. This is done through stimulation of host-cell immune defenses and prevention of adhesion. The microbial colonies enclosed in a slimy layer are also associated with several plant infections and the pathogenic form of human disease.
When the pathogen colonizes and starts to form a film, it gets harder to detect and eliminate. This is especially the case the longer the pathogen is present. The slimy film shields the pathogen from your immune system as well as accelerates the growth and dispersion of the microorganisms throughout your body. The film also provides a favorable environment even for the new pathogens to attach and grow. This paves a path for the development of various diseases within your body.
It is interesting to know how many diseases and chronic health issues go unresolved for years due to similar undetected infections. There are probably several such health conditions which people continue to suffer for decades. If you have yeast, bacterial or parasitic infections, particularly with a history of treatment resistance, then it could indicate a biofilm infection.
Let’s look at some of the common infections related to this category:
One common example includes cystic fibrosis (CF) in which the patients are known to suffer from chronic P. aeruginosa infections. While infecting the lungs, the bacteria undergo a transition from an acute virulent pathogen to a CF-adapted pathogen. This helps the bacteria to remain in the infected lungs for decades. The overproduction of matrix polysaccharide alginate causes the formation of a mucoid (mucus-like) biofilm. This film is often resistant to any removal attempts by the body’s immune system. This mucoid layer can also result in chronic inflammation and severe damage to the lung tissues.
 Despite several barriers, the upper respiratory tract is easily breached by pathogens. Therefore, the ear, nose, and throat are highly vulnerable to acute and chronic infections. Bacterial colony mainly develops through the contamination originating from the use of artificial medical devices such as catheters and valves.
Despite several barriers, the upper respiratory tract is easily breached by pathogens. Therefore, the ear, nose, and throat are highly vulnerable to acute and chronic infections. Bacterial colony mainly develops through the contamination originating from the use of artificial medical devices such as catheters and valves.
Bacteria can adhere to the uroepithelium (lining of the urinary tract) and then form into a colony that can invade the renal tissue. This can cause pyelonephritis (kidney inflammation) and even chronic bacterial prostatitis (swollen prostates). Bacterial colonies can also develop on devices like urethral stents and catheters. Therefore, catheter-associated UTI is a prevalent infection worldwide. Acute UTI caused by bacterial infections can raise the risk of recurrent infection. Some women may even experience recurrent UTI despite their urinary tracts being physiologically and anatomically normal.
Another example of biofilm in the human body is dental plaque and potential dental cavities. Consuming of fizzy carbohydrates such as sugary drinks or treats encourages the dental plaque bacteria to secrete organic acids. When left untreated, the increased acidification by the film can lead to demineralization of the enamel and dental cavities. Furthermore, dental plaque biofilm can also cause periodontal disease.
Biofilm microorganisms are responsible for over eighty percent of the GI infections in humans. Your GI tract consists of physicochemical and nutritional environments making it an ideal ground for the formation and survival of pathogen colonies. These pathogens are also responsible for various chronic infections. Yet, the function, nature and clinical relevance of these pathogen communities are not fully known.
The GI tract has viscoelastic mucus lining for protection. The viscoelastic mucus lining is damaged in patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), excessive inflammation and other conditions. This creates an opportunity for the microorganisms to attach to the surface of the lining and begin the slimy biofilm formation. As the pathogens begin to invade and attach to the epithelium (or lining) it gradually alters and becomes more damaged. This can trigger inflammation in the gut, which releases toxins directly into the bloodstream and interfere with your immune function. These factors contribute to symptoms such as brain fog and autoimmune disorders.
Healthy microbial diversity of your gut is essential for immunity, as well as your mental and physical health. Optimizing your gut function is the foundation to recover from various health conditions including adrenal fatigue. Poor gut health has a direct impact on your immune system thus affecting the Inflammation Circuit of NEM. This can affect your body’s ability in recovering from adrenal fatigue. Removing of the colony of pathogens enclosed in the biofilm from your gut is critical for dealing with GI disorders.
Until the pathogens are completely eradicated, they continue to damage the gut microbiome and allow new pathogens to grow. This is why in most cases, antibiotics and medication often fails to correct IBD, ulcerative colitis, and Crohn’s disease. Though the medication can work for a time, the person continues to experience flare-ups throughout life.
Over twenty percent of individuals infected with Lyme disease caused by burgdorferi, experience prolonged symptoms mostly due to the presence of microbial film or antibiotic resistance. Lyme disease occurs through the transmission of bacteria from ticks, fleas, mites, mosquitoes, and spiders. Statistics reveal that over 3,00,000 people in the U.S each year are affected by this disease. The condition is notoriously difficult to diagnose as it mimics other disorders such as chronic fatigue syndrome, multiple sclerosis (MS), ADHD, fibromyalgia, Alzheimer's disease, and arthritis. The bacteria thrives within the protected colony adding to the difficulty in treating the disease.
Other chronic diseases that can be associated with biofilm include:
Research on this field is gaining more attention due to its widespread association with diseases and the resilience of the bacteria to numerous antimicrobial treatments. Due to the increasing antimicrobial resistance, researchers are now shifting their focus from the bacterial growth causing cell death, towards more novel approaches. Some of the examples of new areas of research include triggering dispersal of the microbial film or exploring ways to prevent the initial formation of the biofilm. An example includes re-engineering the surface of medical devices to make them less vulnerable to the formation of pathogenic colonies.
The traditional approach involves the use of antibiotics. However, research shows that these drugs do not help to eradicate the pathogens. In fact, antibiotics have been shown to contribute to the condition.
There are three steps to successfully remove biofilm:
Fortunately, research has highlighted certain natural alternatives that can help eradicate the pathogen colony. This can be done gently without causing any harsh impact on your body. The antibacterial, antiviral, and immunomodulation properties of plant extracts can help in stopping the growth of the microbial colony in your body.
Lab tests lack the ability to detect pathogens hidden in the protective film. Therefore, it is essential to follow natural microbial film removal protocols for eradicating the stubborn pathogens from your system. Eliminating the colony of pathogens from your body is the foundation for optimal health. Natural remedies are safe and effective without causing any harmful effects on your body.
Microorganisms communicate among themselves through cell signaling which enables them to form colonies. This mechanism is referred to as quorum sensing. It enables the microorganisms to work in groups and adapt to changes in their environment. Therefore, to eradicate the film and its related pathogens from your body, then one must disrupt the quorum sensing communication. There are several natural sources of quorum sensing inhibitors. Natural botanicals may help in eradicating biofilm by breaking quorum sensing among the pathogens.
 Well-known to mankind since ancient times, turmeric is rich in curcumin, a natural compound with potent healing properties. Curcumin has powerful anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, antiviral, anti-fungal, and anti-parasitic properties. Studies also show that curcumin ranks among the top six biofilm-disrupting agents.
Well-known to mankind since ancient times, turmeric is rich in curcumin, a natural compound with potent healing properties. Curcumin has powerful anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, antiviral, anti-fungal, and anti-parasitic properties. Studies also show that curcumin ranks among the top six biofilm-disrupting agents.
The therapeutic use of oregano (especially oregano oil) dates back many centuries. This herb was applied in various ancient medicinal formulations and has been extensively used to eradicate harmful pathogens from the GI tract. Carvacrol, an active compound in oregano, has been documented for its immense health benefits. Carvacrol has potent antibiotic, anti-bacterial, anti-fungal, anti-viral, and anti-parasitic properties which help to inhibit the release of harmful toxins from pathogens including biofilm.
This familiar tonic contains acetic acid which is extremely potent in eradicating harmful bacteria. This acid even cuts through mature microbial films in chronic infections. Although further research on the effects of acetic acid is required, apple cider vinegar serves as an effective and cheap remedy for the eradication of pathogen colonies.
Highly regarded as a potent anti-pathogenic food, garlic is rich in the active component, allicin. Allicin helps to eliminate bacterial resistance and stop biofilm formation. Allicin in garlic is known to disrupt the quorum sensing (or communication) across the pathogens and significantly hinder their growth.
Berberine is a chemical found in plants like the Oregon grape, goldenseal and other herbs. This compound has several profound health benefits. It is believed to be effective in fighting cancer and diabetes. Berberine also has antimicrobial properties which help to hinder the colonization of pathogens in your GI tract.
Propolis is a mixture of substances that originate from a variety of plants. It also has a unique and complex chemical composition. Honey bees collect propolis to seal and protect their hives. High in therapeutic properties, propolis has antiseptic, anti-inflammatory, healing, immunostimulatory, and antimicrobial effects. Propolis serves as an effective fungicide and works to prevent the formation of microbial films.
Neem (Azadirachta indica A. Juss) has always been an integral part of ayurvedic medicine. Loaded with potent therapeutic properties, neem leaves are known to have immense health benefits. The antibacterial, antifungal, and antiseptic properties of neem leaves destroy the pathogens. These leaves also prevent the formation of the protective biofilm around the pathogens.
Considered as catalysts of biochemical processes, proteolytic enzymes assist your body in breaking down of proteins and prove to be highly effective at dissolving biofilms. The proteolytic enzymes, serratiopeptidase and trypsin, can significantly hinder the microbial film formation post-surgery. The combination of proteolytic enzymes, nattokinase and serrapeptase, has been shown to destroy bacterial colonies commonly related to prolonged infections in the body.
The nattokinase enzyme is isolated from natto, a famous fermented soybean product in Japan. The enzyme is known to prevent blood clots, improve blood flow and promote heart health. Serrapeptase enzyme is mostly isolated from the non-pathogenic bacteria Serratia E15 found in silkworms. The enzyme is popular for its powerful anti-inflammatory properties.
Plaque buildup within the tissues can hinder antibiotic treatment. Fibrin, a blood clotting molecule, can form plaques within your tissues. Serrapeptase helps to remove blood clots and plaques from your body. The enzyme can break down fibrin in the dead tissue without damaging the surrounding healthy tissues. This helps in eliminating blood clots and plaques. Thereafter, the antibiotics are able to penetrate into the tissue for effective treatment.
Proteolytic enzymes can also help fight inflammation, improve digestion, promote healing, and reduce muscle soreness. They can also provide relief from inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). Fruits and vegetables like papaya, pineapple, kiwi fruit, yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, asparagus, ginger, and kimchi are some of the dietary sources of proteolytic enzymes. These enzymes can also be taken as supplements in the form of capsules and tablets. Please note that proteolytic enzymes may cause digestive distress in some people. So, always consult with your healthcare professional before beginning a new diet. There are also other essential nutrients that you can explore.
 Activated charcoal is highly regarded for absorbing toxins, and is an important biofilm removal protocol. When antimicrobial compounds break the film and destroy pathogens in your gut, a massive toxic load is released. This load then needs to be absorbed and passed out through the stool.
Activated charcoal is highly regarded for absorbing toxins, and is an important biofilm removal protocol. When antimicrobial compounds break the film and destroy pathogens in your gut, a massive toxic load is released. This load then needs to be absorbed and passed out through the stool.
If the toxic load is not eliminated, it can lead to a Herxheimer reaction in your body. This happens when the toxins are partially dumped from one region of the body, but then start to reabsorb if not properly eliminated. The reaction causes flu-like symptoms, which can be debilitating if proper care is not taken to absorb and eliminate these toxins. Furthermore, toxic overload can contribute to adrenal fatigue and hamper the recovery process. Activated charcoal helps in the absorption of toxins from pathogenic die-off and their elimination from the body.
Biofilm is a colony of microorganisms enclosed in the secreted extracellular polymeric substance (EPS) matrix. Evidence shows that this microbial film is a contributing factor for numerous chronic infections and health conditions. In most cases, these colonies of pathogens remain undiagnosed and unaddressed. This is because the microbes are hidden inside the slimy matrix layer and are resistant to your immune system and antibiotics.
Natural botanicals are shown to be safe and effective in removing these colonies of pathogens from your body. The strategic blend of proteolytic enzymes along with botanicals and activated charcoal can be effective in removing biofilm and successfully fighting chronic infections. The key to a successful natural approach includes the dosage, timing and intensity of such efforts. Those who have AFS needs to be especially careful to avoid detoxification reactions associated with biofilm dissolution. But it is reassuring that you can possibly resolve some long-standing infections and health conditions.
© Copyright 2021 Michael Lam, M.D. All Rights Reserved.
Natural botanicals are safe and effective in eradicating biofilm and related pathogens from your body. However, some people might be allergic to a few of these botanicals. Therefore it is best for them to not use these products to avoid any unpleasant symptoms.
